Table 1. In Vitro Activity of Fusidic Acid.
|
Organism |
N |
Country (year of report) |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC range |
ref |
Gram positive aerobes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Staphylococcus aureusMethicillin susceptible |
162 72 20
|
USA (1987) Japan (1987) Belgium (1990) |
0.03 0.2 0.06 |
0.06 1.56 0.06 |
0.008-0.25 0.1 – 3.13 0.06 – 0.12 |
(39) (40) (92) |
Staphylococcus aureusMethicillin resistant |
185 111 108 100 |
Ireland (1985) USA (1987) Belgium (1990) Germany (1992) |
>32 0.03 0.06 0.125 |
>32 0.12 0.06 4 |
0.03 – 64 0.008 – 4 0.03 – 8 0.03 - 8 |
(92) (32) |
|
Staphylococcus spp Coagulase negative |
100 197 |
Germany (1992) Canada (1995) |
0.25 0.25 |
0.25 0.5 |
0.03 – 8 0.12 - 32 |
(32) (87) |
|
Streptococcus pyogenes |
102 |
France (2000) |
4 |
8 |
1 - 32 |
(43) |
|
Group G streptococci |
69 |
France (2000) |
8 |
8 |
0.25 – 128 |
(43) |
Streptococcus agalactiae |
50 |
France (2000) |
16 |
32 |
1 - 64 |
(43) |
|
Group C streptococci |
10 |
France (2000) |
4 |
16 |
4 - 32 |
(43) |
Enterococcus faecalis |
152 |
Canada (1995 |
4 |
8 |
1.0 - 32 |
(87) |
|
Corynebacterium spp |
118 |
Germany (1977) |
0.04 |
2 |
0.04 – 12.5 |
(30) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gram negative aerobes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bordetella pertussis |
100 |
Canada (1960-81) |
0.1 |
0.2 |
0.03 – 0.5 |
(4) |
Moraxella catarrhalis |
9 |
UK (1962) |
0.12 |
0.12 |
0.06 – 0.12 |
(5) |
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
96 |
Denmark (1968) |
0.6 |
2 |
0.25 - 2 |
(70) |
Neisseria meningitidis |
100 |
UK (1978) |
0.03 |
0.12 |
0.015 – 0.5 |
(48) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mycobacterium spp |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
M. tuberculosis |
170 |
Turkey (2001) |
16 |
16 |
16 - 256 |
(18) |
M. tuberculosis |
64 |
Belgium (1990) |
8 |
16 |
4 - 32 |
(91) |
M. avium |
22 |
Belgium (1990) |
32 |
64 |
1 - > 128 |
(91) |
|
M. chelonei |
17 |
Belgium (1990) |
64 |
128 |
32 - >128 |
(91) |
M. fortuitum |
19 |
Belgium (1990) |
64 |
>128 |
16 - >128 |
(91) |
|
M. kansasii |
19 |
USA (1992) |
32 |
32 |
2.0 - 64 |
(101) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anaerobic bacteria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clostridium difficile |
80 |
Australia (2002) |
0.75 |
2 |
0.125 - 4 |
(45) |
Clostridium perfringens |
39 |
USA (1979) |
0.12 |
0.5 |
£0.06 - 1 |
(79) |
|
Peptostreptococcus anaerobius |
34 |
USA (1979) |
0.25 |
0.5 |
£0.06 - 2 |
(79) |
|
Propionibacterium acnes |
25 |
USA(1979) |
0.25 |
1 |
£0.06 - 2 |
(79) |
Bacteroides fragilis |
100 |
UK (1987) |
2 |
2 |
0.5 - 4 |
(74) |
Prevotella intermedia |
31 |
USA (1979) |
0.25 |
1 |
£0.06 - 1 |
(79) |
|
Porphyromonas asaccharolytica |
31 |
USA (1979) |
0.25 |
1 |
£0.06 - 1 |
(79) |
|
Fusobacterium spp |
15 |
UK (1987) |
1 |
64 |
£0.25 - >128 |
(74) |
· Susceptibility breakpoints have not been determined by NCCLS
· The Comite de l’Antibiogramme de la Societe Francaise de Microbiologie (68)give MIC breakpoints £ 2mg/L = susceptible and >16 mg/L = resistant for non fastidious organisms
· The BSAC (1) MIC breakpoints for staphylococci are £ 1mg/L = susceptible, ³ 2mg/L = resistant
Table 2. Pharmacokinetics of Fusidic Acid/Sodium Fusidate After Oral or IV Administration in Adults.
|
Route |
Number subjects |
Cmax mg/L |
Tmax h |
C 8 h mg/L |
C12 h mg/L |
AUC range |
AUC mg.h/l |
t½ b h |
Cl ml/min |
Vd l/kg |
|
oral (100) |
6 |
31.4 |
3 |
~12 |
|
0-8h |
162 |
|
|
|
|
oral (46) fasting after food |
12 |
30.6
22.7 |
2.2
3.2 |
|
|
0 - ¥
0 - ¥ |
329
276 |
8.9
9.5 |
|
|
|
oral (84) |
8 |
33.3 |
2.1 |
~12.5 |
~10 |
0 - ¥ |
368 |
16.0 |
|
|
|
oral (52) |
10 |
30 |
~2 |
|
8.5 |
0 - ¥ |
315 |
11.0 |
33 |
0.52 (b) |
|
IV (2h infusion) (76) |
8 |
52.4 |
2 |
~15 |
~10 |
|
411 |
9.8 |
21 |
0.3 |
|
IV (2h infusion) (75)
|
12 |
23.6 |
2 |
~11 |
~8 |
|
204 |
14.5 |
42 |
0.46 |
Cmax = peak concentration, Tmax = time to peak concentration, C8h = concentration 8 hours after dosing, C12h = concentration 12 hours after dosing, AUC = area-under-the-curve, t½ß = elimination half-life, Cl = clearance, Vd = volume of distribution, ß = elimination half-life volume of distribution
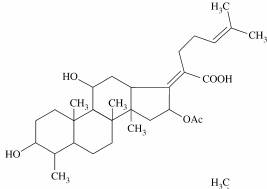
Figure 1. Chemical Structure
