
Table 1. In Vitro Activity Profiles of the Fluoroquinolones (μg/mL)
|
Ciprofloxacin Levofloxacin Gatifloxacin Moxifloxacin Gemifloxacin |
||||||||||
|
Organism |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
|
Gram-Negatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acinetobacter baumannii |
0.5-32 |
>16 |
0.25-4 |
8-16 |
0.12-4 |
8-16 |
0.12-8 |
16-32 |
0.12-8 |
16 - >16 |
|
Enterobacter cloacae |
0.008-0.03 |
0.016-1 |
£0.03 - 0.06 |
0.03-1 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.03-1 |
0.06 |
0.125-0.25 |
0.016-0.03 |
0.03-0.5 |
|
Escherichia coli |
0.008- 0.03 |
0.03-1 |
0.015- 0.03 |
0.06-0.5 |
0.016-0.3 |
£0.03-0.5 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.06-1 |
0.008- 0.016 |
0.03-0.5 |
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
0.008-0.015 |
0.015-0.03 |
0.015 |
0.015-0.06 |
0.008-0.015 |
0.015-0.03 |
0.015-0.03 |
0.06-0.03 |
0.002-0.004 |
0.008-0.03 |
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
0.016- 0.06 |
0.06-2 |
≤0.03-0.06 |
0.25-2 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.06-1 |
0.06- 0.25 |
0.125-1 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.125-1 |
|
Moraxella catarrhalis |
0.03-0.06 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.06 |
0.03 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.03-0.12 |
0.06-0.12 |
0.008-0.015 |
0.008-0.03 |
|
Morganella morganii |
0.008-0.016 |
0.015-2 |
0.031 |
0.125- 0.25 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
0.12-0.25 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.06 |
0.125-4 |
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
0.004-0.5 |
0.004-0.5 |
0.008-0.5 |
0.12-0.5 |
0.12 |
0.25 |
0.008-0.25 |
0.015-0.5 |
0.004-0.12 |
0.06-0.5 |
|
Neisseria meningitidis |
≤0.002-0.008 |
0.004-0.008 |
0.008 |
0.008 |
0.004-0.008 |
0.008 |
0.008 |
0.008-0.015 |
0.004-0.008 |
0.008 |
|
Proteus mirabilis |
0.03-0.06 |
0.03- 2 |
0.03-0.5 |
0.12-2 |
0.12-0.25 |
2-4 |
0.25-1 |
0.25-8 |
0.12-0.25 |
0.25-8 |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
≤0.25-1 |
4 - >16 |
1-4 |
>4 - 16 |
1-4 |
>4 |
2-16 |
8 |
0.5-4 |
>4 - >16 |
|
Serratia marcescens |
0.06-0.25 |
0.5-4 |
0.125 |
0.25-2 |
0.25 |
2 |
0.25 |
4 |
0.125-0.25 |
1-2 |
|
Salmonella spp. |
0.016-0.12 |
0.03- 0.25 |
£0.03-0.06 |
0.25 - 0.5 |
£0.03- 0.06 |
0.06-0.25 |
0.12 |
1 |
0.016-0.03 |
0.016- 0.12 |
|
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia |
2-4 |
8-16 |
0.5-1 |
4-8 |
0.5-1 |
4-8 |
0.5-1 |
2-4 |
0.5-2 |
4-8 |
|
Gram-Positives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
0.5-1 |
0.5 - >4 |
0.125-0.25 |
0.25 - >4 |
0.06-0.12 |
0.12 - >4 |
0.06 |
0.06-2 |
NA |
0.06-8 |
|
MS S. aureus |
0.25-1 |
0.5-4 |
0.12-0.25 |
0.25-2 |
0.06-0.12 |
0.125-0.5 |
0.03-0.12 |
0.06-0.25 |
0.015-0.06 |
0.03-0.12 |
|
MR S. aureus |
1 - >16 |
16 - >128 |
0.25-32 |
8 - >128 |
0.125-8 |
4 - >128 |
0.06 - 2 |
2-128 |
0.03-4 |
2 - >128 |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
1-2 |
2-16 |
0.5-1 |
1-2 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.5 |
0.03-0.25 |
0.12-0.25 |
0.015-0.03 |
0.03-0.06 |
|
Penicillin susceptible |
1-2 |
2-4 |
0.5-1 |
1-2 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
0.125-0.25 |
0.25 |
0.015-0.03 |
0.03-0.06 |
|
Penicillin intermediate |
1-2 |
2-4 |
0.5-1 |
1-2 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
0.125-0.25 |
0.12-0.25 |
0.015-0.03 |
0.03-0.06 |
|
Penicillin resistant |
1-2 |
2-4 |
0.5-1 |
1-2 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.125-0.25 |
0.12-0.25 |
0.015-0.03 |
0.03-0.06 |
|
Viridans Streptococcus |
1-2 |
4 |
1 |
1-2 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.5-1 |
0.25 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.06-0.25 |
|
S. agalactiae |
0.25-1 |
1-2 |
0.5 |
0.5-1 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.125 – 0.25 |
0.25 |
0.03-0.06 |
0.03-0.25 |
|
S. pyogenes |
0.25-1 |
1 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.5-1 |
0.12-0.25 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.06-0.25 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.016-0.06 |
0.03-0.25 |
|
Enterococcus faecalis |
0.5-2 |
1 - >16 |
1 |
³8 - >16 |
0.5-1 |
1-16 |
0.12-0.5 |
0.25 - ³4 |
0.06-0.25 |
2 - ³4 |
|
Enterococcus faecium |
2 - >16 |
4 - >128 |
³8->16 |
³8->16 |
2 - ³16 |
³16 |
2 - 32 |
2 - >32 |
³4 - >16 |
³4 - >16 |
|
Anaerobes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bacteroides fragilis |
4 |
32 |
1-2 |
4-16 |
0.25-1 |
1-4 |
0.125-1 |
1-4 |
0.5 - 1 |
2 - 16 |
|
Clostridium difficile |
8-16 |
16-64 |
4 |
4 - >16 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1-2 |
2 - >16 |
|
Fusobacterium spp. |
1- 4 |
2-16 |
1 |
1-8 |
0.25-1 |
0.25-8 |
0.25-0.5 |
2-4 |
≤0.25 - 4 |
0.5-8 |
|
Peptostreptococcus spp. |
1 |
2 |
0.5-4 |
4 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.06-0.5 |
0.12-1 |
0.03-0.12 |
0.06-2 |
|
Porphyromonas spp. |
0.5 |
2 |
0.25 |
1 |
0.125 |
0.25 |
£0.03-0.25 |
£0.03-0.25 |
0.06 |
0.125 |
|
Prevotella spp. |
1-4 |
2-64 |
0.5-1 |
1-8 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.5-4 |
0.125-0.5 |
0.25-2 |
1-4 |
2-16 |
|
Miscellaneous |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
0.125-2 |
0.125-4 |
0.125-0.5 |
0.125-1 |
0.03-0.12 |
0.03-0.25 |
0.25-0.6 |
0.125-1 |
4 |
8 |
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
1 |
1-2 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.5-1 |
0.06 |
0.12 |
0.06 |
0.06-0.12 |
NA |
0.25 |
|
Chlamydia pneumoniae |
0.5 |
2 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.5-1 |
0.06-0.25 |
0.125-0.25 |
0.06-1 |
0.5-1 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
|
Legionella pneumophila |
0.016-0.03 |
0.016-0.06 |
0.008-0.016 |
0.008-0.016 |
0.008-0.016 |
0.016-0.03 |
0.008-0.016 |
0.008-0.03 |
0.008-0.03 |
0.016-0.03 |
NA: not available
Complied from references (8, 11, 24, 25, 31, 36, 41, 54-57, 65, 72, 75, 81, 82, 85, 96-99, 101, 105, 107, 109-113, 119, 123, 128, 132-134, 142, 165, 173, 190, 215, 216, 218, 219, 222, 224, 225, 232, 237, 249, 255, 271, 272, 281, 285)
Table 2. Pharmacokinetic Parameters of the Fluoroquinolones
|
Parameter |
Norfloxacin |
Ciprofloxacin |
Oflox/Levofloxacin |
Gatifloxacin |
Trovafloxacin |
Moxifloxacin |
Gemifloxacin |
|
Dose (mg) |
400 |
750 |
400/500 |
400 |
300 |
400 |
320 |
|
Peak (mg/mL) |
1.5 |
3.5 |
4.0/6.0 |
3.4 |
4.0 |
4.5 |
1.6 |
|
Peak / 100 mg dose |
0.38 |
0.46 |
1.0/1.2 |
0.85 |
1.32 |
1.12 |
0.5 |
|
Protein bound (%) |
15 |
25 |
25 |
18 |
70 |
50 |
60 |
|
Vdss (L/kg) |
1.7 |
3.2 |
1.45 |
1.7 |
1.1 |
2.7 |
4.18 |
|
t ½ (h) (CrCl 100 mL/min) |
3.3 |
4.0 |
6.0 |
8.4 |
10.0 |
12.7 |
6.1 |
|
t ½ (h) (CrCl 10 mL/min) |
8.0 |
10.0 |
30.0 |
>40 |
12 |
14.5 |
NA |
|
AUC (mg∙h/mL) |
13.6 |
29 |
38/58 |
32 |
41.4 |
48.0 |
9.1 |
|
AUC / 100 mg dose |
1.7 |
1.9 |
11.7 |
8 |
13.8 |
12 |
2.8 |
|
Clrenal (mL/min) |
234 |
250 |
190 |
NA |
10 |
43 |
134 |
|
% Nonrenal |
60 |
40 |
5 |
10 |
90 |
80 |
64 |
|
% Renal |
40 |
60 |
95 |
90 |
10 |
20 |
22 |
|
Bioavailability (%) |
40 |
70 |
99 |
96 |
88 |
86 |
71 |
Compiled from references: (10, 32, 45, 74, 100, 114, 144, 146, 150, 180, 181, 186, 189, 220, 221, 242, 248, 253, 259, 269, 279, 287)
Table 3. Tissue Penetration of the Fluoroquinolones
|
Site |
Dose |
Route |
Frequency |
Time to Ctissue |
Conc. Tissue |
Time to Cplasma |
Conc. Plasma |
Reference |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bile |
500 mg |
po |
bid x 6 |
25-26 h |
4.5 mg/L |
4h |
2.5 |
(64) |
|
Blister, suction |
500 mg |
|
1 x |
|
84.70% |
|
2.26 |
(145) |
|
Lung, parenchyma |
200 mg |
iv |
1 x |
|
3.4 mcg/g |
|
0.6 |
(44) |
|
Lung, pleura |
200 mg |
iv |
1 x |
|
1.7 mcg/g |
|
0.6 |
(44) |
|
Muscle, heart valve |
750 mg |
po |
q 12h x 4 |
1-3 h |
8.3/3.1 mcg/g |
|
11.59/3.95 |
(170) |
|
Muscle, myocardium |
400 mg |
iv |
1 x |
1 h |
31.6/25 mcg/g |
|
6.19/1.73 |
(170) |
|
Prostate, TURP |
200 mg |
po |
tid x 9 |
5.5 h |
1.32/0.64 |
5.5 h |
0.65/0.31 |
(177) |
|
Levofloxacin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bile |
100 mg |
po |
1 x |
2-6 h |
0.49/5.63 |
2-6 h |
0.55/1.63 |
(257) |
|
Norfloxacin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prostate, TURP |
200 mg |
po |
tid x 5 |
|
4.42/1.94 (2.45/7.76) intraoperative |
|
2.89/2.34 (0.87/8.33) intraoperative |
(283) |
|
Ofloxacin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bone |
300 mg |
po |
1 x |
1 h |
1.58/0.06 mcg/g |
1 h |
2.61/0/17 |
(194) |
|
Lung, parenchyma |
600 mg |
po |
1 x |
2 h |
17.7/9.2 mcg/g |
2 h |
8.7/4.2 |
(275) |
|
Muscle, myocardium |
400 mg |
iv |
1 x |
1 h |
8.89/2.16 |
|
15.9/2.5 |
(170) |
|
Prostate, TURP |
200 mg |
po |
tid x 5 |
|
5.51/1.79 (3.62-7.19) intraoperative |
|
5.36/1.28 (3.12-8.24) 30 min preop |
(283) |
|
Moxifloxacin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alveolar macrophages |
400 mg |
po |
1 x |
2.2 h |
56.7 |
2.2 h |
3.2 |
(247) |
|
Bronchial mucosa |
400 mg |
po |
1 x |
2.2 h |
1.29 |
2.2 h |
3.2 |
(247) |
|
Epithelial lining fluid |
400 mg |
po |
1 x |
2.2 h |
20.7 |
2.2 h |
3.2 |
(247) |
|
Maxillary sinus mucosa |
400 mg |
po |
qd x 5d |
3 h |
7.48 |
3 h |
3.58 |
(87) |
|
Blister |
400 mg |
iv |
1 x |
5.6 h |
1.7 |
1 h |
3.7 |
(178) |
|
Skeletal muscle |
400 mg |
iv |
1 x |
1.8 h |
1.2 |
1 h |
3.7 |
(178) |
|
Subcutaneous adipose |
400 mg |
iv |
1 x |
2 h |
1.0 |
1 h |
3.7 |
(178) |
|
Gemifloxacin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alveolar macrophages |
320 mg |
po |
1 x |
|
107 |
|
1.4 |
(203) |
|
Bronchial mucosa |
320 mg |
po |
1 x |
|
9.52 |
|
1.4 |
(203) |
|
Epithelial lining fluid |
320 mg |
po |
1 x |
|
2.69 |
|
1.4 |
(203) |
|
Blister |
320 mg |
po |
1 x |
3.4 h |
0.74 |
1.2 h |
2.3 |
(86) |
Abbreviations: bid = twice daily; iv = intravenously; po = orally; qd = once daily; tid = three times daily
Table 4. Clinical Indications for the Fluoroquinolones and Dosage Regimens
|
Indication |
Agent |
Regimen |
|
Respiratory Infections |
|
|
|
Acute community-acquired pneumonia |
Moxifloxacin |
400 mg q24h iv/po x 7-14 days |
|
|
Gemifloxacin |
320 mg q24h po x 7 days |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
400 mg q24h iv/po x 7-14 days |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
400 mg q12h iv/po x 10 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
500 mg q24 iv/po x 7-14 days 750 mg q24 iv/po x 5 days |
|
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections |
Ciprofloxacin |
500-750 mg q12h po / 400 mg q8-12h iv x 7-14 days |
|
Acute Maxillary Sinusitis |
Moxifloxacin |
400 mg q24 iv/po x 5 days |
|
|
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg po q12h po / 400 mg q12h iv x 10 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
500 mg q12h iv/po x 10-14 days |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
400 mg q24h iv/po x 10 days |
|
Acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis |
Moxifloxacin |
400 mg q24h iv/po x 5 days |
|
|
Gemifloxacin |
320 mg q24h po x 5 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
500 mg q24h iv/po x 7 days |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
400 mg q12h iv/po x 10 days |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
400 mg q24h iv/po x 5 days |
|
Nosocomial pneumonia |
Ciprofloxacin +/- another agent |
400 mg q8 iv x 10-14 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin +/- another agent |
750 mg q24h iv/po x 7-14 days |
|
Urinary Tract Infections (UTI) |
|
|
|
Acute Uncomplicated UTIs |
Ciprofloxacin |
250 mg q12h po x 3 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
250 mg q24h iv/po x 3 days |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
400 mg iv/po single dose or 200 mg q24h iv/po x 3 days |
|
|
Norfloxacin |
400 mg q12h po x 3-10 days |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
200 mg q12h iv/po x 3-7 days |
|
Complicated UTI and pyelonephritis |
Levofloxacin |
250 mg q24h iv/po x 10 days |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
400 mg q24h iv/po x 7-10 days |
|
|
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg q 12h po / 400 mg q12h iv x 7-14 days |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
200 mg q12h iv/po x 10 days |
|
|
Norfloxacin |
400 mg q12h po x 10-21 days |
|
Prostatitis |
Levofloxacin |
500 mg q24h iv/po x 28 days |
|
|
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg q12 h po / 400 mg q12h iv x 28 days |
|
|
Norfloxacin |
400 mg q12h po x 28 days |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
300 mg q12h iv/po x 6 weeks |
|
Venereal Diseases |
|
|
|
Uncomplicated gonococcal infections |
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg po single dose |
|
(Avoid in Asia/Pacific, Hawaii and California) |
Ofloxacin |
400 mg iv/po single dose |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
250 mg iv/po single dose |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
400 mg iv/po single dose |
|
|
Norfloxacin |
400 mg po single dose |
|
Urethritis due to C. trachomatis |
Ofloxacin |
300 mg q12h iv/po x 7 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
500 mg q24h x 7 days |
|
Acute PID |
Ofloxacin (+ metronidazole) |
400 mg q12h iv/po x 10-14 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin (+ metronidazole) |
500 mg q24h iv/po x 10-14 days |
|
Chancroid |
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg q12h po x 3 days |
|
Epididymitis due to enteric gram-negative organisms |
Ofloxacin |
300 mg q12h iv/po x 10 days |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
500 mg q24h iv/po x 10 days |
|
Skin and Bone |
|
|
|
Uncomplicated skin and skin structure infection |
Moxifloxacin |
400 mg q24h x 7 days |
|
|
Ciprofloxacin |
500-750 mg q12h po x 7-14 days 400 mg q8-12h iv |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
500 mg q24h iv/po x 7-10 days |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
400 mg q12h iv/po x 10 days |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
400 mg q24h iv/po x 7-10 days |
|
Complicated skin and skin structure infection |
Levofloxacin |
750 mg q24h iv/po x 7-14 days |
|
Bone and Joint infection |
Ciprofloxacin |
500-750 mg q12h po x 4-6 weeks 400 mg q 8-12h iv |
|
Abdominal infections |
|
|
|
Intra-abdominal infection |
Ciprofloxacin (+ metronidazole) |
500 mg q12h po x 7-14 days 400 mg q12h iv |
|
Infectious diarrhea |
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg q12h x 3-5 days (current recommendations) 500 mg q12h po x 5-7 days (labeled) |
|
|
Ofloxacin |
300 mg q 12h x 3-5 days |
|
|
Norfloxacin |
400 mg q12h x 3-5 days |
|
Typhoid Fever |
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg q12h po x 10 days |
|
Inhalational anthrax (post-exposure) |
Ciprofloxacin |
500 mg q 12h po x 60 days
|
|
Empiric therapy in febrile neutropenia |
Ciprofloxacin (+ piperacillin) |
400 mg q8h iv |
|
|
|
|
Compiled from references (60, 201-206)
Table 5. Side Effect and Drug Interaction Profile of the Fluoroquinolones
|
Parameter |
Norfloxacin |
Ciprofloxacin |
Oflox/Levofloxacin |
Gatifloxacin |
Trovafloxacin |
Moxifloxacin |
Gemifloxacin |
|
GI Upset |
+2 |
+2 |
+1 |
+3 |
+2 |
+3 |
+2 |
|
Photosensitivity |
0 |
0 |
+1 |
+0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
CNS Effects |
+1 |
+1 |
+2 |
+2 |
+3 |
+1 |
+1 |
|
QTc prolongation |
+1 |
+1 |
+1 |
+1 |
+1 |
+1 |
+1 |
|
Theophylline interaction |
+1 |
+1 |
+1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Cation interaction |
+4 |
+4 |
+2 |
+3 |
+1 |
+3 |
+4 |
|
Warfarin interaction |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
For interactions: 0, none; +1, 1-20% change; +2, 20-40% change; +3, 40-60% change; +4, > 60% change. For GI upset,QTc prolongation, photosensitivity, and CNS effects: 0, none; +1, 1-3%; +2, 3-5%; +3, 5-10%; +4, > 10%.
Adapted from references:(21, 46, 185, 195, 201-207)
Table 6. Dosing During Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (Ciprofloxacin)
|
CVVH (Continuous venovenous hemofiltration): 200mg IV q12h |
|
CVVHD (Continuous venovenous hemodialysis): 200-40mg IVq12h |
|
CVVHDF (Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration) 200-400mg g IV q12h |
Note: CVVH is mainly for fluid removal alone. Many institutions will employ more CVVHD
or CVVHDF which combine dialysis with fluid removal.
Table 7: Dosing during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy(Moxifloxacin)
|
CVVH (Continuous venovenous hemofiltration): 400mg q12h |
|
CVVHD (Continuous venovenous hemodialysis): 400mg IV q12h |
|
CVVHDF (Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration) 400mg IV q12h |
Note: CVVH is mainly for fluid removal alone. Many institutions will employ more CVVHD or CVVHDF which
combine dialysis with fluid removal.
Figure 1.
Structure Activity Relationship of the Fluoroquinolones

Reproduced from reference (50), with permission.
Originally published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy1994;33(4): 685-706.
Figure 2. Structure of the Fluoroquinolones
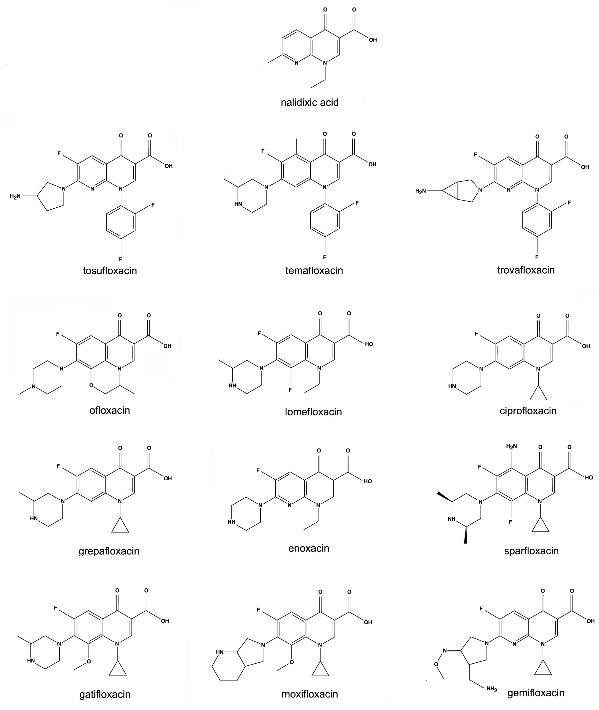
Figure 3. Time to Eradication Versus AUIC

Relationship between the day of bacterial eradication and AUIC values above 250 for cefmenoxime (●) and cirprofloxacin (■). At the same AUIC range above 250, ciprofloxacin eradicates bacteria earlier in therapy.
Figure 4. Relationship Between Serum Concentrations and Selected MIC Values
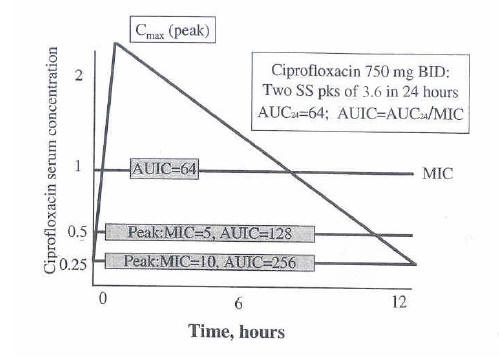
Relationship between serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin and selected MIC values. At each value of MIC, the AUIC and peak to MIC ratio is calculated. Values are based on a 750-mg dose given twice daily.