Table 1: Main Diagnostic Approaches in Clinical Manifestations Associated with B19V Infection
|
Clinical Manifestations |
Clinical Specimens |
Laboratory Diagnosis |
|
Erythema infectiosum |
serum |
IgG/IgM |
|
Arthropathy |
serum |
IgG/IgM |
|
Transient aplastic crisis |
serum |
DNA by PCR |
|
Pure red cell aplasia |
serum/bone marrow aspirates |
DNA by PCR |
|
Hydrops fetalis |
maternal serum |
DNA by PCR, IgG/IgM |
|
fetal specimens (amniotic fluid cells/cord blood, bioptic tissues) |
DNA by PCR and ISH |
|
|
Chronic syndromes and persistent B19V infection |
serum |
DNA by quantitative PCR |
Table 2: Comparison of Major Commercial Assays for the Detection of B19V DNA and Antibodies
|
Real Time PCR assays |
Assay characteristics |
References |
|
Roche LightCycler Parvovirus B19 Quantification Kit (Roche Diagnostics, Germany) |
Quantitative detection of B19V genotype 1. Genotype 2 and 3 are not detected |
8, 21, 35, 57 |
|
RealArt Parvo B19 LC PCR Kit (Artus GmbH, Germany) |
Quantitative detection of B19V genotype 1 and 2 (underestimation of genotype 3) |
8, 35, 57 |
|
EIA assays |
|
|
|
Parvovirus B19 EIA IgG/IgM (Biotrin, Ireland) |
Baculovirus-produced VP2 antigens for detection of B19V IgG Baculovirus-produced VP2 antigens in capture-format for detection of B19V IgM |
29,43, 63, 81, 92 |
|
Parvovirus B19 EIA IgG/IgM Denka Seiken (Japan) or Medac Diagnostika (Germany) |
Baculovirus-produced VP1 and VP2 antigens for detection of B19V IgG Baculovirus-produced VP1 and VP2 antigens in capture-format for detection of B19V IgM |
29, 81 |
|
recomWell Parvovirus B19 IgG/IgM (Mikrogen Germany) |
Escherichia coli expressed VP1 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae produced VP2 antigens for the detection of B19V IgG and IgM |
29, 43, 92 |
|
NovaLisaTM Parvovirus B19 recombinant (NovaTec Immundiagnostica, Germany) |
Escherichia coli expressed VP1 and baculovirus-produced VP2 antigens for detection of B19V IgG and IgM |
89 |
|
RidaScreen Parvovirus B19 IgG/IgM (R-Biopharm, Germany) |
Escherichia coli expressed VP1 and VP2 antigens for detection of B19V IgG and IgM |
38 |
|
Immunofluorescence assays |
|
|
|
Parvovirus B19 IFA (Biotrin, Ireland) |
Baculovirus-produced VP1 antigens for detection of B19V IgG and IgM |
38 |
|
Immunoblot assays |
|
|
|
recomLine Parvovirus B19 IgG [Avidity]/IgM (Mikrogen Germany) |
Escherichia coli expressed VP1, VP2, NS antigen fragments and yeast-produced VP2 for detection of B19V IgG and IgM. Optionally available additional reagent for IgG Avidity |
43, 92, 111
|
|
RidaBlot Parvovirus B19 IgG/IgM (R-Biopharm, Germany) |
Escherichia coli expressed VP1, VP2, NS antigen fragments for detection of B19V IgG and IgM |
38 |
Table 3: Treatment for B19V Infection
|
Clinical Manifestations |
Treatments |
References |
|
Arthropathy |
Anti-inflammatory drug |
22, 77 |
|
Transient aplastic crisis (TAC) |
Blood transfusion |
53 |
|
Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) |
IVIG |
76, 126, 93, 40
|
|
Hydrops fetalis |
Blood transfusion |
44 |
|
IVIG |
86, 115 |
|
|
Chronic arthritis and persistent B19V infection |
IVIG |
103, 125, 77 |
|
Chronic fatigue syndrome and persistent B19V infection |
IVIG |
68 |
|
Meningoencephalitis |
IVIG |
66, 58 |
The current recommendation is IVIG 0,4g/Kg per 5 days in immunocompetent patients. An empirical maintenance treatment with a single –day infusion
of 0.4g/Kg IVIG every 4 weeks may control B19V in immunosuppressed patients (27).
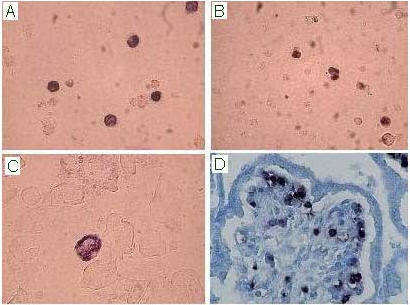
Figure 1: In situ hybridisation assay for the detection of B19V nucleic acids on bone marrow (A),
fetal cord blood (B), amniotic fluid cells (C) and placental bioptic sample (Methyl Green counterstain;
D). B19V infected cells show a nuclear purple/blue precipitate.
