Table 1. Principal activity of ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole and voriconazole against human fungal pathogens. Detailled clinical indications are discussed in the corresponding text paragraphs.
|
|
KETO |
ITRA |
FLU |
VORI |
· Opport. yeasts |
|
|
|
|
|
- Candida albicans |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
- Candida tropicalis |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
- Candida glabrata |
+ |
+/- |
+/- |
+ |
|
- Candida krusei |
+/- |
+/- |
0 |
+ |
|
- Cryptococcus neoformans |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
· Opport. hyaline moulds |
|
|
|
|
|
- Aspergillus spp. |
0 |
+ |
0 |
+ |
|
- Fusarium spp. |
0 |
0 |
0 |
+/- |
|
- Scedosporium spp. |
+/- |
+/- |
0 |
+/- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
· Dermatophytes |
+ |
+ |
+/- |
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
· Dimorphic moulds |
|
|
|
|
|
- Histoplasma capsulatum |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
- Coccidioides immitis |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
- Blastomyces dermatitidis |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
- Parracoccidioides brasiliensis |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
- Sporothrix schenkii |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
|
- Penicillium marneffei |
+ |
+ |
+/- |
+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
· Zygomycetes |
|
|
|
|
|
- Mucorales |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
- Entomophthorales |
0 |
+/- |
0 |
? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
· Dematiaceous moulds |
+/- |
+/- |
0 |
+/- |
Rating: 0, no activity; +/-, variable activity; + consistent activity
Table 2. Pharmacokinetic parameters of ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole and voriconazole in healthy adult volunteers at steady state after oral daily dosing with 200 mg (Data compiled from references 18, 26, 46, 84, 87, 88, 96, 103,107, 179).
|
|
Ketoconazole |
Itraconazole |
Fluconazole |
Voriconazole |
|
Oral bioavailability (%)
|
75 |
55 |
>90 |
>90 |
|
Tmax (h) |
1-4 |
1.5-4 |
1-2 |
1-2 |
|
Cmax (ug/mL) |
3-5 |
10 |
10 |
1.5-2.3 |
|
AUC0-24h (ug.h/mL) |
12 |
15.4 |
170 |
19.4 |
|
Protein binding (%) |
> 85 |
>95 |
<12 |
58 |
|
VD (L/kg) |
1.16 |
10.7 a |
0.7-0.8 |
2-4 |
|
Principal route of elimination |
Hepatic |
Hepatic |
Renal |
Hepatic |
|
T 1/2 beta |
6-10 |
21-37 |
27-37 |
6 |
|
CL (mL/min.kg) |
2.75 |
3.80 |
0.23 |
n/a |
|
Unchanged drug in urine (%) |
2-4 |
<1 |
80 |
<2 |
|
Relative CSF levels (%) |
<10 |
<1 |
50-90 |
50-80 |
a calculated from an intravenous dose of 100mg.
Table 3a. Profile of common or important adverse effects of ketoconazole and itraconazole in adults at usual dosages (≤ 400mg/day) and dose-limiting toxicity (modified from reference 41, 96 and 253)
|
|
Ketoconazole |
Itraconazole |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
Nausea, vomiting (<10%); Abdominal pain, anorexia (<5%) |
Nausea, vomiting (<5%); Diarrhea (3%); abd. pain (<2%) |
|
|
|
|
|
Skin and appendages |
Pruritus, rash (<5%), potentially exfoliative |
Pruritus, rash (<5%), potentially exfoliative |
|
|
|
|
|
Liver and biliary system |
Elevation of hepatic transaminases (<10%): hepatitis (rare) |
Elevation of hepatic transaminases (<5%): hepatitis (rare) |
|
|
|
|
|
Kidney |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Bone marrow |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Immunologic |
Anaphylaxis reported |
Anaphylaxis reported |
|
|
|
|
|
Endocrine system |
Adrenal insufficiency; decreased testosterone synthesis; menstrual irregularities and alopecia in women (all rare) |
Syndrome of mineralocorticoid excess: Pedal edema; decreased testosterone syn- thesis (all rare) |
|
|
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
? |
Congestive heart failure (rare) |
|
|
|
|
|
Special senses |
Photophobia |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Nervous system |
Headache |
Headache, dizziness |
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum tolerated dosage in clinical trials and limiting events |
> 800 mg/day: - Endocrinologic effects - Gastrointestinal intolerance |
600-800 mg/day - Endocrinologic effects - Gastrointestinal intolerance |
Table 3b. Profile of common or important adverse effects of fluconazole and voriconazole in adults at usual dosages (≤ 400mg/day) and dose-limiting toxicity (modified from references 41, 96 and 253)
|
|
Fluconazole |
Voriconazole |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders |
Nausea, vomiting (<5%); Abdominal pain, diarrhea (<2%) |
Nausea, vomiting (<5%); Abdominal pain (<10%) |
|
|
|
|
|
Skin and appendages |
Pruritus, rash (<2%), potentially exfoliative |
Pruritus, rash (<10%), potentially exfoliative |
|
|
|
|
|
Liver and biliary system |
Elevation of hepatic transaminases (<7%): hepatitis (rare) |
Elevation of hepatic transaminases (<15%): hepatitis (rare) |
|
|
|
|
|
Kidney |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Bone marrow |
Neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia reported |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
Immunologic |
Anaphylaxis reported |
Anaphylaxis reported |
|
|
|
|
|
Endocrine system |
- |
Adrenal insufficiency (rare) |
|
|
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
? |
Cardiac arrhythmias (<5%) |
|
|
|
|
|
Special senses |
- |
Altered/enhanced perception of light; photophobia, blured vision (<30%) |
|
|
|
|
|
Nervous system |
Headache, seizures |
Halluzinations, confusion (<10%); headache |
|
|
|
|
|
Maximum tolerated dosage in clinical trials and limiting events |
1200 mg/day: - Hepatotoxicity - CNS-toxicity |
up to 800 mg/day (10mg/kg/day) have been tolerated without dose-limiting events for a period of 14 days |
Table 4. Drug-drug interactions of ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole and voriconazole
|
Mechanism and Drug Involved |
Azole Involved |
Comment |
|
|
|
|
|
Decreased plasma concentration of azole compounds: |
|
|
|
Decreased absorption of triazole - Antacids, H2-antagonists, omeprazole, sucralfate, didanosine, grapefruit juice |
KETO, ITRA (capsules) |
Take antacids and antifungal agent at least 2 hours apart** |
|
|
|
|
|
Increased metabolism of triazole -Isoniazid, rifampin, rifabutin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine
-Nevirapin, efavirenz |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI**
VORI |
Potential for therapeutic failure; increased potential for hepatotoxicity**
Potential for therapeutic failure** |
|
|
|
|
Increased plasma concentration of azole compounds:-Ritonavir, indinavir -Delavirdine, efavirenz -Erythromycin, clarithromycin |
KETO, ITRA, VORI VORI KETO, ITRA |
Monitor closely for toxicity and adverse events |
|
|
|
|
|
Increased plasma concentration of coadministered compounds: -Terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, mizolastine, dofetilide, quinidine, pimozide, domperidon -Lovastatin, simvastatin, atorvastatin
|
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI
KETO, ITRA, VORI |
Contraindicated (QTc prolongation)
Contraindicated (rhabdomyolysis) |
|
-Triazolame, PO midazolame |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI |
Contraindicated (oversedation) |
|
-Ergotamin, dihydroergotamin |
KETO, ITRA, VORI |
Contraindicated(ergotism) |
|
-Alprazolam, brotizolam, IV midazolam |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI |
Monitor closely |
|
-Buspirone, alfentanil, sildenafil |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-Haloperidol |
ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-Phenytoin |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI |
Monitor levels ** |
|
-Carbamazepine |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor levels |
|
-Rifampin, rifabutin |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI |
Monitor closely |
|
-Clarithromycin |
ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-Indinavir, ritonavir,saquinavir |
KETO, ITRA, VORI |
Monitor closely |
|
-Vincristine, vinblastine, vindesine |
KETO, ITRA, VORI |
Avoid concom. use ** |
|
-Busulfan |
KETO, ITRA |
Avoid concom. use |
|
-Docetaxel |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-Trimetrexate |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-All-trans retinoic acid |
FLU |
Monitor closely |
|
-Dihydropyridine, verapamil |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-Nifedipine, felodipine |
ITRA, FLU |
Monitor closely |
|
-Cyclosporine A, tacrolimus, sirolimus |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI |
Monitor levels ** |
|
-Sulfonylurea drugs |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI |
Monitor closely ** |
|
-Methylprednisolone |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-Warfarin |
KETO, ITRA, FLU, VORI |
Monitor prothromb. time** |
|
-Digoxin |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor levels |
|
-Ebastin, reboxetin |
KETO, ITRA |
Monitor closely |
|
-Zidovudine; theophyllin |
FLU |
Monitor closely |
|
-Omeprazole |
VORI |
Omeprazole dose reduction |
**major clinical relevance; compiled form references 65,92,96,99,116,253
Table 5. Dosing During Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (Fluconazole)
|
CVVH (Continuous venovenous hemofiltration): 200-400mg q24h |
|
CVVHD (Continuous venovenous hemodialysis): 400-800mg q24h |
|
CVVHDF (Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration) 400-800mg q24h |
Note: CVVH is mainly for fluid removal alone. Many institutions will employ more CVVHD
or CVVHDF which combine dialysis with fluid removal.
Note: A dose of 800mg is appropriate if the dialysate flow rate is and/or if treating fungal
species with relative azole resistance such as C. glabrata
Table 6. Dosing during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (Voriconazole)
|
CVVH (Continuous venovenous hemofiltration): 1-2g IV q12h |
|
CVVHD (Continuous venovenous hemodialysis): 2g IV q12h |
|
CVVHDF (Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration) 2g IV q12h |
Note: CVVH is mainly for fluid removal alone. Many institutions will employ more
CVVHD or CVVHDF which combine dialysis with fluid removal.
Note: The oral bioavailability of voriconazole is estimated to be 96%.
Consider 2 loading doses of 6mg/kg PO q12h
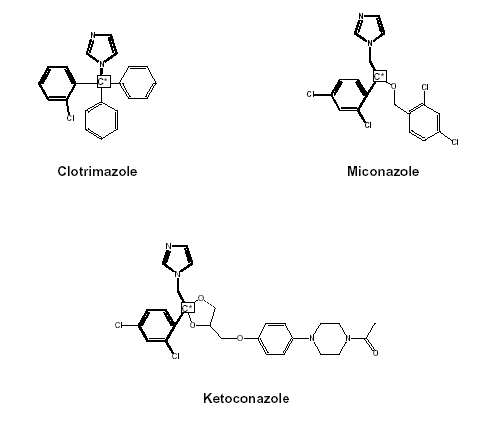
Figure 1. Structural formulas of clotrimazole, miconazole and ketoconazole

Figure 2. Ergosterol-biosynthesis and the target of the class of antifungal azoles
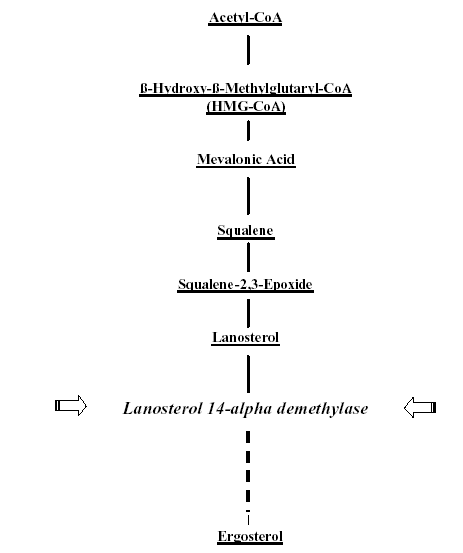
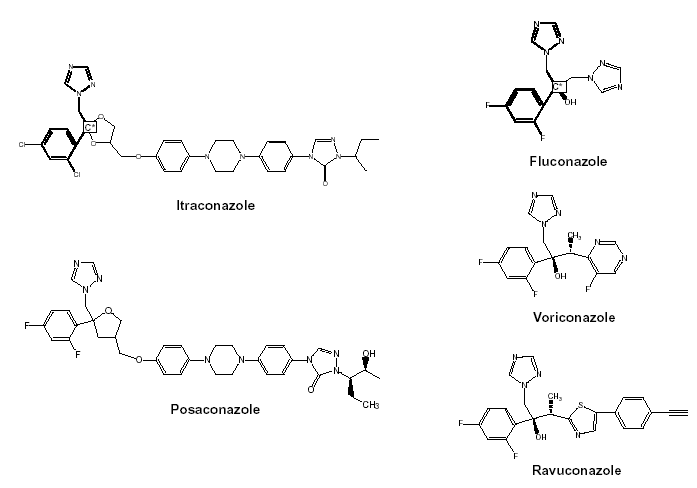
Figure 3. Structural formulas of itraconazole, fluconazole, voriconazole and two investigational triazoles, posaconazole and ravuconazole