Figure. Penicillin Structure
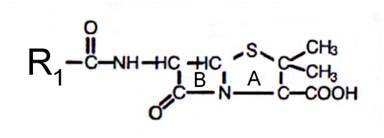


A – thiazolidine ring; B – beta-lacam ring; R1- acyl side chain
Table 1. Classification of Penicillins
|
Class and compounds |
Trade names1 |
Availability |
|
Natural penicillins |
|
|
|
penicillin G potassium |
Pfizerpen |
Parenteral: 5, 20 mu vials |
|
phenoxymethyl penicillin |
various generics |
Tablets: 250, 500mg Solution: 125mg/5 mL, 250mg/5 mL |
|
penicillin G procaine |
Wycillin |
Parenteral: 600,000 u/mL |
|
penicillin G benzathine |
Bicillin L-A, Permapen |
Parenteral: 300,000u/mL, 600,000u/mL |
|
penicillin G procaine/ penicillin G benzathine combination |
Bicillin C-R |
Parenteral: 150,000u/150,000 u/mL, 150,000/450,000 u/mL, 300,000/30,000 u/mL |
|
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins |
|
|
|
methicillin |
Staphcillin |
no longer available |
|
nafcillin |
various generics |
Parenteral: 20 mg/mL vials |
|
oxacillin |
Bactocill |
Capsules: 250, 500mg Solution: 250mg/5mL Parenteral: 500mg, 1, 2, 4 g vials |
|
cloxacillin |
various generics |
Capsules: 250, 500mg Solution: 125mg/5 mL |
|
dicloxacillin |
Dynapen |
Capsules: 250, 500mg Suspension: 62.5 mg/5 mL |
|
Aminopenicillins |
|
|
|
ampicillin |
Principen |
Capsules: 250, 500 mg Suspension: 125 mg/5 mL, 250 mg/5 mL Parenteral: 125, 250, 500 mg, 1, 2 g vials |
|
amoxicillin |
Amoxil, Trimox |
Capsules: 250, 500 mg Chewable tablets: 125, 250, 400 mg Film-coated tablets: 500, 875 mg Suspension: 50mg/mL, 125 mg/5 mL, 200 mg/5 mL, 250 mg/5 mL, 400 mg/5 mL |
|
bacampicillin |
Spectrobid |
no longer available |
|
Carboxypenicillins |
|
|
|
carbenicillin |
Geocillin |
Tablets: 382 mg |
|
ticarcillin |
Ticar |
Parenteral: 1, 3, 6 g vials |
|
Ureidopenicillins and piperazine penicillin |
|
|
|
azlocillin |
Azlin |
no longer available in U.S. market |
|
mezlocillin |
Mezlin |
no longer available in U.S. market |
|
piperacillin |
Pipracil |
Parenteral: 2, 3, 4g vials |
1 = not all formulations
are available with every brand
Table 2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC50) of Specific Organisms
| MIC-50 (µg/mL) | ||||||
| Organism | Penicillin G | Penicillin V | Oxacillin | Ampicillin Amoxicillin |
Ticarcillin |
Mezlocillin Piperacillin |
| Gram-Positive aerobes | ||||||
| Enterococcus sp. | 2.0 | 4.0 | >32 | 0.5 | 64 | 2 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ||||||
| (Non Penicillinase producing) | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.4 | 0.06 | 1.0 | 0.06 |
| (Penicillinase-producing) | >32 | >32 | 1.6 | >32 | 32 | 32 |
| Staphlyococcus epidermidis | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 0.4 | 0.02 |
| Viridans streptococci | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.125 |
| Listeria monocytogenes | 0.25 | 0.25 | >4 | 0.25 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Gram-negative aerobes | ||||||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeaea | 0.25 | 1.0 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.015 | |
| Neisseria meningitidis | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| Escherichia coli | 64 | 128 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 32 | 128 | 4 | 0.5 | 2 | 1 |
| Indole + P. mirabilis | >500 | >500 | >128 | 64 | 4 | 1 |
| Hemophilus influenzaea | 0.4 | 6.3 | 25 | 0.25 | 0.012 | 0.03 |
| Salmonella sp. | 8 | 128 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Shigella sp. | 16 | 64 | 4 | |||
| Serratia marcescens | >128 | >128 | >128 | >500 | 16 | 88 |
| Klebsiella sp. | >128 | >128 | >128 | 64 | >64 | 16 |
| Enterobacter sp. | >128 | >128 | >128 | 128 | 16 | 8 |
| Citrobacter sp. | >128 | >128 | >128 | 32 | 2 | 2 |
| Acinetobacter sp. | >128 | >128 | >128 | 16 | 8 | 16 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >128 | >128 | >128 | >500 | 16 | 8 |
| Anaerobes | ||||||
| Peptostreptococcus | 0.1 | >32 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | <0.1 | >64 | <0.1 | 0.5 | <0.1 | |
| Clostridium perfringens | 0.5 | >64 | <0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Bacteroides fragilis | 16 | >64 | 16 | 16 | 32 | |
a non-beta-lactamase producing strains
Table 3. Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC-90) of Specific Organisms
|
MIC-90 (µg/mL) |
|||||
|
Organism |
Penicillin G |
Oxacillin |
Ampicillin Amoxicillin |
Ticarcillin |
Mezlocillin Piperacillin |
|
Gram-Positive aerobes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enterococcus sp. |
2.0 |
>100 |
4 |
128 |
4 |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Non Penicillinase producing) |
0.03 |
3.1 |
0.125 |
1.0 |
0.06 |
|
(Penicillinase-producing) |
>32 |
6.3 |
>32 |
32 |
32 |
|
Staphlyococcus epidermidis |
|
|
|
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
0.03 |
0.8 |
0.02 |
1 |
0.02 |
|
Viridans streptococci |
|
|
|
8 |
0.25 |
|
Streptococcus pyogenes |
0.015 |
0.4 |
0.03 |
0.25 |
0.125 |
|
Listeria monocytogenes |
0.5 |
>4 |
0.5 |
4 |
0.5 |
|
Gram-negative aerobes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeaea |
0.5 |
12.5 |
0.06 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
|
Neisseria meningitidis |
0.06 |
6.3 |
0.25 |
0.03 |
0.03 |
|
Escherichia coli |
64 |
>128 |
>256 |
>256 |
256 |
|
Proteus mirabilis |
32 |
>128 |
>256 |
128 |
16 |
|
Indole + P. mirabilus |
>500 |
>128 |
>256 |
>256 |
64 |
|
Hemophilus influenzaea |
4 |
100 |
0.5 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
Salmonella sp. |
16 |
>128 |
>256 |
>256 |
>256 |
|
Shigella sp. |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
Serratia marcescens |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>256 |
128 |
|
Klebsiella sp. |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
500 |
16 |
|
Enterobacter sp. |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
>256 |
128 |
|
Citrobacter sp. |
>128 |
>128 |
128 |
256 |
8 |
|
Acinetobacter sp. |
>128 |
>128 |
64 |
64 |
128 |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
128 |
32 |
|
Anaerobes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Peptostreptococcus |
1.0 |
>32 |
8.0 |
2.0 |
4.0 |
|
Fusobacterium nucleatum |
1.0 |
>64 |
16.0 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
|
Clostridium perfringens |
0.5 |
>64 |
<0.1b |
0.5 |
0.5 |
|
Bacteroides fragilis |
>64 |
>64 |
>64 |
128 |
128 |
a non-beta-lactamase producing strains
b amoxicillin’s MIC90 is 0.5.
Table 4. In Vitro Post-Antibiotic Effect of Selected Penicillins
|
|
S. aureus |
S. pneumoniae |
E. faecalis |
|
penicillin G |
2-3.5 hrs |
2.5-3.5 hrs |
2.5-3.5 hrs |
|
ampicillin |
2-2.5 hrs |
2-6 hrs |
0.5-2.5 hrs |
|
nafcillin |
1.5-2 hrs |
ND |
ND |
|
piperacillin |
£0.5 hr |
ND |
£0.5 hr |
ND = no data
Table 5. Prevalence of Resistance of Organisms to Penicillins
|
Organism |
Prevalence |
|
Gram-positive |
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniaea,b |
Intermediate pcn resistance 11-28% Highly pcn resistant 11-33% |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
Pcn resistant >95% Methicillin resistant (nosocomial) 23-38% |
|
Gram-negative |
|
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
ampicillin 1-64% |
|
Moraxella catarrhalis |
up to 85% |
|
Escherichia coli |
ampicillin 30-50% |
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
1.2-38% |
|
Neisseria meningitidis |
up to 20% |
|
Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producers |
|
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
up to 24% |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
piperacillin 5-30% |
a intermediate resistant strains have MICs of 0.12-1.0 µg/mL
highly resistant strains have MICs of ³2.0 µg/mL
b United States data
Table 6. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Penicillins
|
Drug |
dose |
peak serum conc.1 |
% bioavailability |
half-life (hours) |
%ppb2 |
|
Natural penicillins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
benzylpenicillin |
2g |
20 µg/mL |
na |
0.5 |
50-60 |
|
penicillin G oral3 |
400,000 u |
0.3 µg/mL |
15-30 |
0.5 |
|
|
penicillin VK |
250 mg |
3 µg/mL |
60 |
0.5 |
75-85 |
|
procaine pen G IM |
300,000 u |
0.9 µg/mL |
|
|
|
|
benzathine pen G IM |
1.2 mu |
0.09 µg/mL |
|
|
|
|
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
nafcillin IV |
1g |
20 µg/mL |
na |
0.5-1.0 |
90 |
|
oxacillin IV |
500mg |
52-63µg/mL |
na |
0.5-0.7 |
94 |
|
oxacillin oral |
500mg |
5-7 µg/mL |
30-35% |
0.5-0.7 |
|
|
cloxacillin oral |
500mg |
7.5-14µg/mL |
50 |
0.5 |
95 |
|
dicloxacillin oral |
500mg |
10-17µg/mL |
37 |
0.8 |
98 |
|
Aminopenicillins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ampicillin IV |
1g |
40 µg/mL |
na |
1-1.3 |
20 |
|
ampicillin oral |
1g |
3 µg/mL |
30-50 |
1-1.3 |
|
|
amoxicillin oral |
1g |
7.5 µg/mL |
80 |
1-1.3 |
20 |
|
Extended-spectrum penicillins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
carbenicillin IV |
3g |
223 µg/mL |
na |
1.1 |
50 |
|
carbenicillin oral |
1g |
9 µg/mL |
30 |
|
|
|
ticarcillin |
3.5g |
210 µg/mL |
na |
1.2 |
45 |
|
mezlocillin |
3g |
263 µg/mL |
na |
0.8 |
16-42 |
|
piperacillin |
4g |
240 µg/mL |
na |
1.0 |
16 |
1 = data complied from product package information and Donowitz 1988.
2 = % plasma protein bound
3 = no longer commercially
available in the US
Table 7. Guidelines for Adult and Pediatric Dosing of Penicillins
|
Drug |
Normal adult dosec |
Normal pediatric dosec |
Dosage adjustment in renal impairmentd,e |
|
Natural penicillins |
|
|
|
|
benzylpenicillin (penicillin G) |
enterococcal endocarditis: 4-6 mub IV q4h Streptococcal meningitis: 2-3 mu IV q4h Streptococcal infection: 2mu IV q4-6h |
£ 1week and > 2kg: 20,000-50,000 u/kg IV q8h £ 1 week and £ 2kg: 20,000-50,000 u/kg IV q12h > 1 week and £ 2kg: 25,000-65,000 u/kg IV q8h > 1 week and > 2kg: 25,000-65,000 u/kg IV q6h > 1month and < 12 years, severe infection: 40,000-60,000 u/kg IV q4-6h > 12 years: usual adult dose |
CrCL 10-50 mL/min: Increase dosing interval to q6-8h CrCL < 10 mL/min: Increase dosing interval to q12h |
|
|
anthrax (setting of bioterrorism): 4 mg IV q4h |
<12 years: 50,000 u/kg IV q6h >12 years: usual adult dose |
|
|
|
neurosyphilis: 3-4 mu IV q4h |
|
|
|
penicillin VK |
Streptococcal pharyngitis: 500 mg po bid-tid for 10 days Lyme disease: 250-500mg po qid for 10-30 days |
> 1 month: 15-62.5 mg/kg/day po in 3-6 divided doses Lyme disease and < 9 years: 25-50 mg/kgday po in 3 divided doses for 10-30 days |
Little data available. Adjust dose if CrCL < 10 mL/min. |
|
procaine penicillin G (PPG) |
Streptococcal infection: 600,000-1.2 mu IM qd for 10 days |
neonates: 50,000 u/kg/day IM >1 month and < 12 years: 25,000-50,000 u/kgday IM ³ 12 years: usual adult dose |
Not necessary |
|
benzathine penicillin G |
early syphilis: 2.4 mu IM group A strep infection and prophylaxis of recurrent rheumatic fever: 1.2 mu IM |
<27kg: 300,000-600,000 u IM ³27 kg: 1.2 mu IM |
Not necessary |
|
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins |
|
|
|
|
nafcillin |
500mg-1g po q4-6h 1-2g IV q4-6h |
> 1 month: 50-100 mg/kg/day po in 3-4 divided doses > 1 month: IV data limited, 100-200mg/kg/day in 4-6 divided doses |
CrCL < 10 mL/min: Extend dosage interval to q8-12 hrs |
|
oxacillin |
500mg-1g po q4-6h 1-2g IV q4-6h |
> 1 month and < 40kg: 50-100 mg/kg/day po or IV in 4 divided doses ³ 40 kg: usual adult dose |
CrCL < 10 mL/min: use lower range of usual dose |
|
cloxacillin |
250-500mg po q6h |
> 1 month and < 20 kg: 50-100 mg/kg/day po in 4 divided doses ³ 20 kg: usual adult dose |
|
|
dicloxacillin |
125-250 mg po q6h |
> 1 month and < 40 kg: 12.5 - 25 mg/kg/day po in 4 divided doses ³ 40 kg: usual adult dose Staphylococcal osteomyelitis: 50-100 mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses |
not necessary |
|
Aminopenicillins |
|
|
|
|
ampicillin |
250-500mg po q6h 1-2g IV q4h |
³ 1 month and < 40 kg: 50-200 mg/kg day IV in 4-6 divided doses < 1 week: 25 mg/kg IV/IM q 8-12h ³ 1 week and < 1 month: 25 mg/kg IV/IM q6-8h > 40 kg: usual adult dose |
CrCL 10-50 mL/min: Extend dosing interval to q 6-12h CrCL < 10 mL/min: Extend dosing interval to q8-16h |
|
amoxicillin |
500mg po q12h or 250-500mg po q8h or 875mg po q12h |
> 1 month and < 20 kg: 20-40 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses > 20 kg: usual adult dose |
CrCL 10-50 mL/min: Consider extending dosing interval to q12h. CrCL < 10 mL/min: Extend dosing interval to q12-24h. |
|
Extended-spectrum penicillins |
|
|
|
|
carbenicillin |
382-764 mg po qid |
No data |
No data |
|
ticarcillin |
3g IV q4h |
> 1 month and < 40 kg: 100-300 mg/kg/day in 4-6 divided doses ³40 kg: usual adult dose |
CrCL 30-60 mL/min: 2g q4h CrCL 10-30 mL/min: 2g q8h CrCL < 10 mL/min: 2g q12h Supplement after HD: 3g |
|
mezlocillin |
3-4g IV q4-6h |
< 1 week: 75 mg/kg q12h ³ 1 week and < 1 month: 75 mg/kg q6-8 hrs ³ 1 month and < 12 yrs: 50-75 mg/kg q4h ³ 12 years: usual adult dose |
CrCL 10-50 mL/min: 1.5-3g q6-8h CrCL < 10 mL/min: 1.5-2g q8h Supplement after HD: 3-4g |
|
piperacillin |
3-4g IV q4-6h |
1 month -12 years: 50 mg/kg q4h |
CrCL 20-40 mL/min: 3-4g q8h CrCL < 20 mL/min: 3-4g q12h Supplement after HD: 1g |
a = intramuscular
b = million units
c = These dosages are ranges of acceptable doses. The lower range of usual dose is generally used for mild infection, upper range for severe infection (e.g. meningitis, endocarditis). Higher dosages than recommended may be used in certain circumstances. Clinical judgment should be used when dosing and prescribing information for the specific drugs should be consulted for more information.
d = clinical judgment should be utilized when making decisions regarding dosage adjustment in renally impaired patients, taking into account severity of renal impairment, site of infection, expected length of therapy, organism isolated, etc.
e = data complied using McEvoy 2003 AHFS Drug Information and product package inserts
HD = hemodialysis
Table 8. Approximate Cost of Typical Therapeutic Regimens of Selected Penicillins1
|
Drug |
Dosing regimen |
Cost1 |
|
Oral agents |
|
|
|
ampicillin |
500mg po q6h x 10d |
$5.00 |
|
penicillin VK |
500mg po q8h x 10d |
$4.00 |
|
amoxicillin |
500mg po q8h x 10d |
$5.00 |
|
Long-acting agents |
|
|
|
procaine penicillin G |
1.2 mu IM x1 |
$5.00 |
|
benzathine penicillin G |
2.4mu IM x1 |
$15.00 |
|
Intravenous agents |
|
|
|
ampicillin |
2g IV q4h x 10d |
$57.00 |
|
penicillin G potassium |
2 mu IV q4h x 10d |
$21.00 |
|
penicillin G sodium |
2 mu IV q4h x 10d |
$158.00 |
|
oxacillin |
1g IV q6h x 10d |
$109.00 |
|
ticarcillin |
3g IV q4h x 10d |
$375.00 |
|
piperacillin |
4g IV q6h x 10d |
$390.00 |
1 = drug acquisition costs for Albany Medical
Center Hospital, Albany, New York.