Table 14. Dosing Recommendations for Parenteral Cephalosporins in Patients with Renal Dysfunction
|
Agent |
Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) |
Dosage |
Post-Hemodialysis Dose |
|
First-generation |
|
|
|
|
Cefazolin |
> 55 35-54 11-34 ≤ 10 |
Usual 0.5 g q8h or 1 g q12h 0.5 g q12h or 1 g q24h 0.5 g q18-24 h |
0.5-1 g |
|
Second-generation |
|
|
|
|
Cefuroxime |
> 20 10-20 < 10 |
Usual 0.75 g q12h 0.75 g q24h |
0.75 g |
|
Cefamandole |
> 80 50-80 25-50 10-25 2-10 |
Usual 1.5 g q4h or 2 g q6h 1.5 g q6h or 2 g q8h 1 g q6h or 1.25 g q8h 1 g q12h |
1 g |
|
Cefoxitin |
> 50 30-50 10-29 < 10 |
Usual 1-2 g q8-12h 1-2 g q12-24h 0.5-1 g q24-48h |
1 g |
|
Cefotetan |
> 30 10-30 < 10 |
Usual 0.5 g q12h or 1-2 g q24h 0.5 g q24h or 1-2 g q48h |
1 g |
|
Third-generation |
|
|
|
|
Cefotaxime |
> 50 10-50 < 10 |
Usual 1-2 g q8-12h 1-2 g q24h |
1 g |
|
Ceftizoxime |
>80 50-79 5-49 < 5 |
Usual 0.75-1.5 g q8h 0.5-1 g q12h 0.5 g q24h or 1 g q48h |
1 g |
|
Ceftazidime |
> 50 30-50 10-29 < 10 |
Usual 1 g q12h 1 g q24h 1 g q48h |
1 g |
|
Fourth-generation |
|
|
|
|
Cefepime |
> 60 30-60 11-29 < 10 |
Usual 1-2 g q24h 0.5-1 g q24h 0.25-0.5 g q24h |
0.5-1 g |
|
Advanced-generation |
|
|
|
|
Ceftaroline |
> 50 31-50 15-30 End stage renal disease, including hemodialysis |
Usual 400 mg q12h 300 mg q12h 200 mg q12h |
200 mg |
Table 15. Adverse Effects Associated with Cephalosporins
|
Adverse Effect |
Frequency (%) |
|
Thrombophlebitis |
1-2 |
|
Hypersensitivity reactions |
|
|
Maculopapular rash |
1-3 |
|
Urticaria |
1-3 |
|
Pruritis |
|
|
Anaphylaxis/angioedema |
< 0.02 |
|
Serum sickness (↑ with cefaclor and cefprozil) |
|
|
Eosinophilia |
1-7 |
|
Hematologic reactions |
|
|
Reversible neutropenia |
< 1 |
|
Leukopenia |
0.5-5 |
|
Thrombocytosis |
2-5 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
0.5-5 |
|
Coombs’ test positive |
1-5 |
|
Coagulation abnormalities |
|
|
Hypoprothrombinemia (related to agents with MTT side chain) |
|
|
Impaired platelet aggregation |
|
|
Gastrointestinal reactions |
|
|
Diarrhea, non-specific; C. difficile-related |
2-5 |
|
Abnormal liver function tests (mild) |
1-7 |
|
Biliary sludge (ceftriaxone-dose-related; may be more common in children) |
20-45 |
|
Nephrotoxicity |
|
|
Interstitial nephritis |
Rare |
|
Decrease in GFR |
1-6 |
Table 16. Dosing during Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
|
CVVH (Continuous venovenous hemofiltration): 1-2g IV q12h |
|
CVVHD (Continuous venovenous hemodialysis): 2g IV q12h |
|
CVVHDF (Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration) 2g IV q12h |
Note: CVVH is mainly for fluid removal alone. Many institutions will employ more
CVVHD or CVVHDF which combine dialysis with fluid removal.
Figure 1. The Basic Cephalosporin (cephem) Nucleus

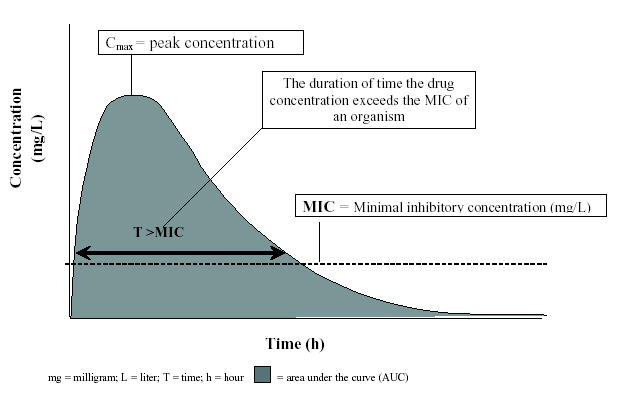
Figure 2. A Concentration Versus Time Curve Depicting the Pharmacodynamic Parameter T>MIC