Table 1. In Vitro Susceptibility Testing of Several Multi-Drug Resistant and Susceptible Gram-Positive Organisms Against Daptomycin. The MIC 90 and MIC Range in the Respective Studies are Seen Below.
|
Organism |
No. |
MIC90 |
MIC range |
Reference |
|
Enterococcus faecalis |
|
|
|
|
|
Vancomycin – Susceptible |
220 |
1.0-2.0 |
0-.015-4.0 |
|
|
Vancomycin – Resistant |
231 |
0.5-4.0 |
0.25-8.0 |
|
|
Enterococcus faecium |
|
|
|
|
|
Vancomycin – Susceptible |
358 |
1.0-4.0 |
0.5-8.0 |
|
|
Vancomycin – Resistant |
249 |
1.0-4.0 |
0.25-4 |
|
|
Listeria monocytogenes |
25 |
4.0 |
2.0-8.0 |
(39) |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
|
|
|
Glycopeptide - Intermediate |
22 |
4 |
0.5-16 |
|
|
Methicillin – Resistant |
711 |
0.25-1 |
0.06-2.0 |
|
|
Methicillin – Susceptible |
1473 |
0.5-1.0 |
0.015-2.0 |
|
|
Vancomycin – Intermediate |
47 |
1 |
0.0625-2.0 |
|
|
Vancomycin – Resistant |
1 |
n/a |
0.25 |
(24) |
|
Staphylococcus coagulase negative |
|
|
|
|
|
Methicillin - Resistant |
954 |
0.5-1.0 |
0.004-1.0 |
|
|
Methicillin - Susceptible |
728 |
0.25-2.0 |
0.03-0.5 |
|
|
Staphylococcus epidermidis |
|
|
|
|
|
Methicillin – Resistant |
65 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.12-1.0 |
|
|
Methicillin – Susceptible |
66 |
0.25 |
0.06-1.0 |
|
|
Staphylococcus species |
|
|
|
|
|
S. haemolyticus |
56 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.03-1.0 |
|
|
S. saprophyticus |
30 |
0.5 |
0.25-1.0 |
(90) |
|
Streptococci species |
|
|
|
|
|
Group G Streptococci |
10 |
0.06 |
0.015-0.06 |
(90) |
|
Streptococcus milleri |
30 |
1.0 |
0.25-1.0 |
(90) |
|
Streptococcus pyogenes |
340 |
0.06 |
0.015-0.5 |
|
|
Viridans Streptococci |
126 |
1.0-2.0 |
0.016-8.0 |
|
|
Streptococcus agalactiae |
81 |
0.25 |
0.12-.025 |
(53) |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
50 |
0.25 |
0.06-0.25 |
(53) |
|
Penicillin Intermediate |
389 |
0.25-1.0 |
0.008-1.0 |
|
|
Penicillin Resistant |
267 |
0.25-1.0 |
0.015-1.0 |
|
|
Penicillin Susceptible |
1166 |
0.25-0.5 |
0.015-0.5 |
|
MIC90 = minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of strains tested in mg/L.
Table 2. Susceptibility Breakpoints. The Following Susceptibility Interpretive Criteria Breakpoints are Approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and are Based Upon Several in vitro and in vivo Activity Studies.
|
TENTATIVE SUSCEPTIBILITY BREAKPOINTS |
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
|
||
|
|
Susceptible |
Intermediate |
Resistant |
|
Enterococcus sp. |
< 4 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Staphylococcus sp. |
< 1 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Streptococcus sp. (other than Streptococcus pneumoniae) |
< 1 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Disk Diffusion for above organisms (except Enterococcus sp.) |
> 16mm |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Disk Diffusion for Enterococcus sp. |
> 11mm |
N/A |
N/A |
Table 3. Comparative Inhibitory Activity of Daptomycin, Linezolid, Quinupristin/Dalfopristin and Vancomycin against Selected Gram-Positive Organisms.
|
|
|
Daptomycin MIC90 range |
Linezolid MIC90 range |
Quinupristin/ Dalfopristin MIC90 range |
Vancomycin MIC90 range |
|
Enterococcus faecalis |
Vancomycin – Susceptible |
1-2 |
1-4 |
8-32 |
1-4 |
|
Vancomycin – Resistant |
0.5-4 |
2-4 |
16-32 |
R |
|
|
Enterococcus faecium |
Vancomycin – Susceptible |
1-4 |
2-4 |
0.5-4 |
1.5-2 |
|
Vancomycin – Resistant |
1-4 |
2-4 |
0.5-16 |
R |
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus (1,3,4,6,7,10,12,19,26,28,36,37,41,44,46, 47,49,53,65,66,71,72,82,86,88,95) |
Methicillin – Susceptible |
0.5-1 |
2-4 |
0.25-2 |
0.5-1 |
|
Methicillin – Resistant |
0.25-1 |
1-4 |
1.00.2-2 |
0.5-2 |
|
|
Vancomycin–Intermediate |
0.5-1 |
1-2 |
0.25 |
I |
|
|
Vancomycin – Resistant* |
1 |
2 |
<1 |
R |
|
|
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci |
Methicillin-Susceptible |
0.25-2 |
2 |
0.1-1 |
1-2 |
|
Methicillin-Resistant |
0.5-1 |
1-2 |
0.25-1 |
1-2 |
|
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae |
Penicillin Susceptible |
0.25-0.5 |
1.5-2 |
0.39-1 |
0.25-0.5 |
|
Penicillin Intermediate |
0.25-1 |
1 |
0.5-2 |
0.25-1 |
|
|
Penicillin Resistant |
0.25-1 |
1 |
0.5-2 |
0.5-1 |
|
|
Anaerobic Organisms (43) |
Actinomyces group |
4 |
0.5 |
0.25 |
1 |
|
Clostridium difficile |
1 |
16 |
16 |
2 |
|
|
Clostridium perfringens |
0.5 |
2 |
1 |
0.5 |
|
|
Lactobacillus sp. |
16 |
8 |
2 |
32 |
|
|
Peptostreptococcus sp. |
0.06-1 |
1-2 |
1-2 |
0.25-1 |
|
|
Propionibacterium sp. |
2 |
1 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
|
Gram positive bacilli Organisms (43) |
Corynebacterium jeikeium |
0.25 |
0.5 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
Corynebacterium sp. |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0.5 |
MIC90 = minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% of strains tested
* based upon 2 isolates in Michigan and Pennsylvania
Table 4. Mean Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Daptomycin in Healthy Volunteers After 30 Minute Intravenous Infusions.
|
Parameter |
Daptomycin |
|
Dose |
4mg/kg |
|
Cmax (mg/L) |
77.5 |
|
t1/2 (h) |
8 |
|
t1/2 renal failure* (h) |
28 |
|
% serum protein binding |
90 |
|
Vd (L) |
7 |
|
AUC0-24 (mg • hr/L) |
468 |
|
Systemic clearance (ml/h/kg) |
8.2 |
|
Urinary excretion (%) |
60 |
* Patients with renal failure
Table 5. Reported Adverse Events in a Large Scale Clinical Trial Evaluating Daptomycin Vs. A Comparator of Vancomycin or a Semi-Synthetic Penicillin in a Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Phase III Randomized Clinical Trial (8,9).
|
Adverse Event |
Daptomycin (n=534) |
Comparator (n=558) |
|
Constipation |
6.2% |
6.8% |
|
Nausea |
5.8% |
9.5% |
|
Injection site reaction |
5.8% |
7.7% |
|
Headache |
5.4% |
5.4% |
|
Diarrhea |
5.2% |
4.3% |
|
Insomnia |
4.5% |
5.4% |
|
Rash |
4.3% |
3.8% |
|
Vomiting |
3.2% |
3.8% |
|
Abnormal liver function tests |
3.0% |
1.6% |
|
Pruritus |
2.8% |
3.8% |
|
Elevated CPK |
2.8% |
1.8% |
|
Fungal Infections |
2.6% |
3.2% |
|
Hypotension |
2.4% |
1.4% |
|
Urinary Track Infections |
2.4% |
0.5% |
|
Renal Failure |
2.2% |
2.7% |
|
Dizziness |
2.2% |
2.0% |
|
Anemia |
2.1% |
2.3% |
|
Dyspenia |
2.1% |
1.6% |
|
Fever |
1.9% |
2.5% |
|
Limb pain |
1.9% |
2.0% |
|
Hypertension |
1.1% |
2.0% |
|
Dyspepsia |
0.9% |
2.5% |
|
Arthralgias |
0.9% |
2.2% |
Table 6. Dosing During Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy
|
CVVH (Continuous venovenous hemofiltration): 4 or 6mg/kg IV q48h |
|
CVVHD (Continuous venovenous hemodialysis): 4 or 6mg/kg IV q48h |
|
CVVHDF (Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration) 4 or 6mg/kg IV q48h |
Note: CVVH is mainly for fluid removal alone. Many institutions will employ more CVVHD or CVVHDF which
combine dialysis with fluid removal.
Figure 1. Structure. Daptomycin is a novel 13-member amino acid cyclic lipopeptide compound that contains a water-soluble hydrophilic core with a lipophilic tail. The lipophilic tail exerts itself into the cytoplasmic membrane of the gram-positive cell wall.

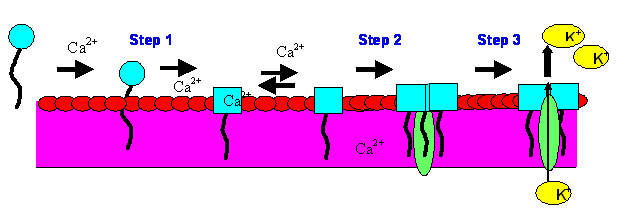
Daptomycin
Figure 2. Daptomycin’s Mechanism of Action. Step 1: Calcium-dependent binding/insertion of the lipophillic tail into gram-positive cyotplasmic membrane. Step 2: Oligomerization/channel formation occur. Step 3: Ion leakage and collapse of organism leading to cell death.