Table 1. Sites of Colonization and Infections in Humans, Non-Group A and Non-Group B Streptococcal Pathogens
Streptococcus
Normal residence
Infection
Group C and G
(pyogenes-like or large colony forming organisms)
GGS (S. equi, S. equisimillis,
S. zooepidemicus)
oropharyngeal flora,
vagina
rectum
skin
S. canis is a zoonotic agent
pharyngitis
skin infection
bacteremia
endocarditis
meningitis
osteomyelitis
septic arthritis
respiratory tract infection
puerperal infection
neonatal sepsis
toxic shock-like syndrome
rhabdomyolysis
Viridans groups of streptococci39
oropharynx, gastrointestinal tract, and genital tract
endocarditis
infections in neutropenic patients
Mitis group
S. mitis
S. gordonii
S. oralis
S. sanguis
S. parasanguis
(S. pneumoniae)*
dental plaques, oropharynx and gastrointestinal tract
Bacteremia, endocarditis, meningitis
ARDS
Anginosus or "S. mlleri" group
S. anginosus
S. constellatus
S. intermedius
oropharynx, gastrointestinal tract, and vaginal flora, skin
pyogenic infections, brain, liver, and appendiceal abscesses
Associated with polymicrobial infection
Endocarditis
Salivarius group
S. salivarius
S. thermophilus
S. vestibularis
tongue and gastrointestinal tract
A frequent contaminant and rarely cause infection, such as bacteremia, meningitis
Bovis group
S. bovis
S. equinus
S. alactolyticus
oropharynx, gastrointestinal, genital tract
bacteremia and endocarditis in patients with malignancies of gastrointestinal tract especially with biotype I
meningitis
Mutans group
S. mutans
S. rattus
S. cricetus
S. downei
S. sobrinus
S. macacae
dental plaques and tooth surfaces
dental caries
endocarditis
"Nutritionally variant streptococci" renamed Abiotrophia
A. adjacensA. defectivus
oropharynx
endocarditis,
sepsis
pancreatic abscess
otitis media
eye infections (conjunctivitis, and crystalline keratopathy)
*Taxonomically, S. pneumoniae is a member of VGS but it is not considered a VGS organism.
Table 2. Susceptibility of Group C Streptococci from Various Reports
|
Antibiotic |
No. of Strains |
MIC90 mg/mL |
MIC Range |
Reference |
|
Penicillin G |
17 |
0.15 |
0.04-0.15 |
|
|
|
125 |
0.05 |
<0.006-0.05 |
|
|
Amoxicillin |
125 |
0.05 |
<0.006-0.1 |
|
|
Ampicillin |
125 |
0.1 |
<0.006-0.2 |
|
|
Cephalothin |
125 |
0.2 |
0.05-0.39 |
|
|
Cephalexin |
125 |
3.13 |
0.39-6.25 |
|
|
Cefaclor |
125 |
1.56 |
0.39-6.25 |
|
|
Meropenem |
48 |
0.06 |
<0.016-0.12 |
|
|
Erythromycin |
125 |
0.1 |
0.0125-0.39 |
|
|
Ciprofloxacin |
8 |
1 |
0.5-1 |
|
|
Clinafloxacin |
8 |
0.5 |
0.13-0.5 |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
8 |
0.25 |
0.13-0.25 |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
8 |
1 |
0.5-1 |
|
|
Moxifloxacin |
8 |
0.13 |
0.06-0.13 |
|
|
Trovafloxacin |
8 |
0.25 |
0.13-0.25 |
|
|
Vancomycin |
48 |
0.5 |
0.06-1.0 |
|
|
Linezolid |
48 |
2.0 |
0.5-2.0 |
|
|
Quinupristin-dalfopristin |
48 |
.25 |
0.06-0.25 |
Table 3. Susceptibility of Group G Streptococci from Various reports.
|
Antibiotic |
MIC90 mg/mL |
MIC Range |
Reference |
|
Penicillin |
0.017 |
.0025-.04 |
|
|
|
0.05 |
<.0063-0.1 |
|
|
Amoxicillin |
0.05 |
<.0063-0.2 |
|
|
Ampicillin |
0.1 |
<.0063-0.2 |
|
|
|
0.022 |
.01-0.04 |
|
|
Oxacillin |
0.12 |
0.06-0.12 |
|
|
Piperacillin |
0.06 |
0.03-1.0 |
|
|
Cephalothin |
0.2 |
0.025-0.2 |
|
|
|
0.09 |
0.04-0.156 |
|
|
Cefotaxime |
0.027 |
0. 005-0.04 |
|
|
|
0.022 |
0.01-0.04 |
|
|
Ceftazidime |
0.5 |
0.03-32.0 |
|
|
Cefoxitin |
0.27 |
0.156-0.312 |
|
|
Cephalexin |
3.13 |
0.1-6.25 |
|
|
Cefaclor |
3.13 |
0.1-6.25 |
|
|
Cefpodoxime |
0.12 |
not reported |
|
|
0.06 |
<0.016-0.06 |
||
|
Vancomycin |
1.13 |
0.312-2.5 |
|
|
|
0.64 |
0.312-1.25 |
|
|
|
.25 |
.25-0.5 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
0.25-4.0 |
|
|
|
0.5 |
0.12-0.5 |
|
|
Teicoplanin |
.06 |
<0.03-0.5 |
|
|
|
0.25 |
0.25-0.5 |
|
|
Linezolid |
2.0 |
0.12-2.0 |
|
|
Quinupristin-dalfopristin |
0.25 |
0.125-0.25 |
|
|
Erythromycin |
0.06 |
<0.03-0.12 |
|
|
|
1.94 |
0.037-2.5 |
|
|
Clarithromycin |
.06 |
<0.03-0.12 |
|
|
Clindamycin |
0.5 |
<0.03-0.5 |
|
|
|
1.1 |
0.06-2 |
|
|
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole |
0.12 |
0.25 |
|
|
Chloramphenicol |
5.5 |
0.3-10 |
|
|
Ciprofloxacin |
1.0 |
0.5-2.0 |
|
|
|
2.0 |
0.25-2.0 |
|
|
|
0.5 |
0.25-0.50 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.25-1 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.15-2.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.5-2.0 |
|
|
Levofloxacin |
0.5 |
0.25-1.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.25-1 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
0.25-4.0 |
|
|
Sparfloxacin |
1.0 |
0.25-1.0 |
|
|
|
0.5 |
0.12-2.0 |
|
|
Clinafloxacin |
0.06 |
<0.03-0.12 |
|
|
|
0.25 |
0.06-0.25 |
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
0.25 |
0.13-0.25 |
|
|
|
0.25 |
0.12-0.5 |
|
|
Moxifloxacin |
0.13 |
0.06-0.13 |
|
|
Trovafloxacin |
0.13 |
0.06-0.25 |
*Isolates from cancer patients
Table 4. Susceptibility of Group C and Group G Streptococci (49,62,84)
|
Antibiotic |
No. of Strains |
MIC90 mg/mL MIC Range |
Reference |
|||
|
|
Penicillin G |
44 |
0.03 |
0.03-0.06 |
||
|
|
Cephalothin |
44 |
0.06 |
0.03-0.5 |
||
|
|
Cefotaxime |
44 |
0.12 |
0.03-0.25 |
||
|
|
Piperacillin |
44 |
0.03 |
0.03-0.5 |
||
|
|
Azlocillin |
44 |
0.06 |
0.03-0.25 |
||
|
|
Vancomycin |
44 |
0.12 |
0.03-0.5 |
||
|
|
Erythromycin |
44 |
1.0 |
0.03-1.0 |
||
|
|
|
20 |
0.5 |
0.12-1.0 |
||
|
|
Clarithromycin |
20 |
0.25 |
0.06-1.0 |
||
|
|
Azithromycin |
20 |
0.5 |
0.12-1.0 |
||
|
|
Quinupristin/dalfopristin |
20 |
0.5 |
0.06-1.0 |
||
|
|
Gatifloxacin |
10 |
0.125 |
0.125 |
||
|
|
Clinafloxacin |
10 |
0.25 |
0.125-0.25 |
||
|
|
Ofloxacin |
10 |
2 |
0.5-2.0 |
||
|
|
Levofloxacin |
10 |
1 |
0.5-1.0 |
||
|
|
Ciprofloxaxin |
10 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
||
|
|
Sparfloxacin |
10 |
2 |
0.125-2 |
||
|
|
Trovafloxacin |
10 |
0.25 |
0.125-0.25 |
||
Table 5.
Recommended
Therapy for VGS Infections
Endocarditis due to penicillin susceptible viridans streptococci and Streptococcus bovis (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration <0.1 mg/mL).
Native valve infection: Use any of the following:
1. Penicillin G 12-18 million units per day in continuous drip or 6 divided dose plus gentamicin 3 mg/kg IV as single dose or 3 divided doses for 2 weeks.
2. Penicillin G 12-18 million units per day in continuous drip or 6 divided dose for 4 weeks.
3. Ceftriaxone 2 g IV or IM daily for 4 weeks.
4. Vancomycin 30 mg/kg not to exceed 2 g IV in 2 divided doses for 4 weeks.
Prosthetic valve infection.
Penicillin or vancomycin as 2 and 3 for 6 weeks plus gentamicin at the same dose as above for at
least 2 weeks.
Endocarditis due to viridans streptococci and Streptococcus bovis relatively resistant to
penicillin G (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration >0.1 mg/ml and <0.5 mg/ml)*
1. 18 million U/24 h IV either continuously or in six equally divided doses for 4 weeks plus
gentamicin 3 mg/kg IV as single dose or 3 divided doses for 2 weeks.
2. Vancomycin 30 mg/kg not to exceed 2 g IV in 2 divided doses for 4 weeks.
Endocarditis due to viridans streptococci with (MIC >0.5 mg/ml) or nutritionally variant streptococci
1. Aqueous crystalline penicillin G sodium, 18-30 million U/24 h IV either continuously or in six equally divided doses or, ampicillin sodium 12 g/24 h IV either continuously or in six divided doses plus gentamicin sulfate 1 mg/kg IM or IV every 8 h for 4-6 weeks*
2. Vancomycin** hydrochloride 30 mg/kg per 24 h IV in two equally divided doses, to exceed 2g/24 h unless serum levels are monitored plus gentamicin sulfate (similar dose as above) for 4-6 weeks*
For patients with prosthetic valve endocarditis due to streptococcus
Treat as resistant streptococcus (MIC >0.5 mg/ml) for 6-8 weeks
For patients with bacteremia without endocarditis due to viridans group of streptococcus and NVS.
1. Penicillin G 12-18 million units IV continuously or in 6 divided doses for 2 weeks.
2. Ceftriaxone 2 g IV or IM daily for 2 weeks
3. Clindamycin 300 mg IV or PO q8h for weeks***
4. Vancomycin 30 mg/kg not to exceed 2 g IV in 2 divided doses for 2 weeks.
For patients with meningitis due to viridans group of streptococcus or NVS
1. Ceftriaxone 2 g IV or IM daily or cefotaxime 2 g IV q6h for 2 weeks
2. Penicillin 18-30 million units IV in 6 divided doses for 2 weeks
3. Vancomycin 30 mg/kg not to exceed 2 g IV in 2 divided doses for 2 weeks
For patients with mixed infection where viridans group of streptococcus or NVS is found
1. Beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations at the recommended dose
2. Imipenem 500-750 mg every 6-8 hours IV.
3. Above agents or clindamycin plus gentamicin.
*4-week therapy recommended for patients with symptoms <3 months in duration; 6-week therapy
recommended fro patients with symptoms greater than 3 months in duration plus
**Vancomycin therapy is recommended for patients allergic to beta-lactams; cephalosporins is not
acceptable unless shown to be effective by susceptibility testing
***Clindamycin susceptibility should be checked.
Table 6. Prophylactic Regimens for Dental, Oral, Respiratory Tract or Esophageal
Procedures (From Recommendations
Of The American Heart Association, 1997) ( 17 )
|
Agent |
Regimen* |
|
|
Standard general prophylaxis |
Amoxicillin |
Adults: 2.0 g; children 50 mg/kg orally 1 h before procedure |
|
Unable to take oral medications |
Ampicillin |
Adults: 2.0 g IM or IV; children: 50 mg/kg IM or IV within 30 minutes before procedure |
|
Allergic to penicillin |
Clindamycin, or Cephalexin** or cefadroxil** Azithromycin or clarithromycin
|
Adults: 600 mg; children: 20 mg/kg orally 1 h before procedure Adults: 2.0 g; children: 50 mg/kg orally 1 h before procedure
Adults: 500 mg; children: 15 mg/kg orally 1 h before procedure |
|
Allergic to penicillin and unable to take oral medications |
Clindamycin or Cefazolin |
Adults: 600 mg; children: 20 mg/kg orally 1 h before procedure Adults: 1.0 g; children: 25 mg/kg IM or IV within 30 min before procedure |
*Total children’s dose should not exceed adult dose
**Cephalosporins should not be used in individuals with immediate-type hypersensitivity reaction
(urticaria, angioedema, or anaphylaxis) to penicillins
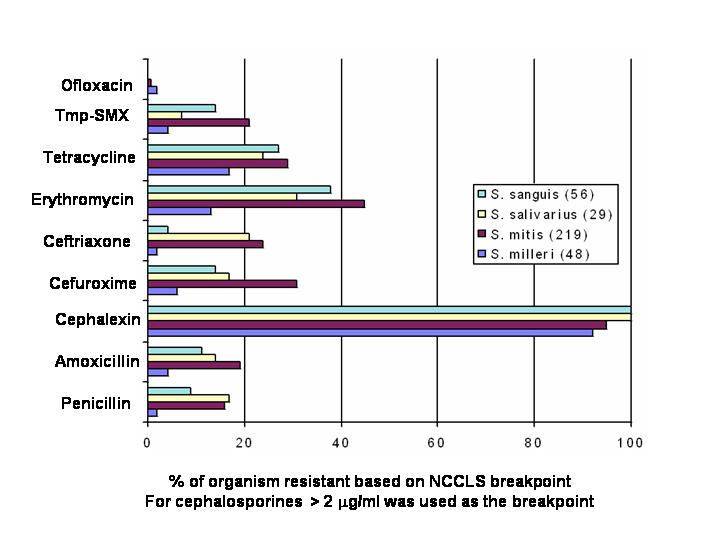
Figure 1. In Vitro Activities of Selected Antimicrobial Agents Versus 4 Streptococcal Species Streptococcal Isolates From 43 U.S. Medical Centers From 1993-4. (Modified from Doern et al (22))