Table 1: Definitions of Pneumococcal Resistance to ß-Lactam
Antibiotics
|
Antibiotic
|
Definition
by MIC (μg/ml) 1 |
||
|
Susceptible |
Intermediate |
Resistant |
|
|
Penicillin |
£ 0.06 |
0.1 - 1 |
³ 2 |
|
Amoxicillin |
£ 2 |
4 |
³ 8 |
|
Cefotaxime,
Ceftriaxone,
Cefepime:
non-meningitis
meningitis |
£ 1
£ 0.5 |
2
1 |
³ 4
³ 2 |
|
Cefaclor |
£ 1 |
2 |
³ 4 |
|
Cefprozil |
£ 2 |
4 |
³ 8 |
|
Cefpodoxime |
£ 0.5 |
1 |
³ 2 |
|
Ceftibuten |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Cefixime |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Cefuroxime
sodium (parenteral) |
£ 0.5 |
1 |
³ 2 |
|
Cefuroxime
axetil (oral) |
£ 1 |
2 |
³ 4 |
|
Imipenem |
£ 0.12 |
0.25-0.5 |
³ 1 |
|
Meropenem |
£ 0.25 |
0.5 |
³ 1 |
1.
Susceptibility definitions are from ref [150]
Table 2: Pneumococcal (N=1531)
Resistance (%) to Antibiotics in 33 Centers in the
|
Antibiotic |
Intermediate
1 |
Resistant
1 |
Overall
Nonsusceptible |
|
Penicillin |
12.7 |
21.5 |
34.2 |
|
Age 0-5 yr |
13.7 |
28.9 |
42.6 |
|
Cefaclor |
2.9 |
29.5 |
32.4 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
10.3 |
14.4 |
24.7 |
|
Cefuroxime |
2.0 |
25.3 |
27.3 |
|
Clindamycin |
0.3 |
8.9 |
9.2 |
|
Erythromycin2 |
0.5 |
25.7 |
26.2 |
|
Levofloxacin |
0.4 |
0.3 |
0.7 |
|
TMP-SMX |
5.6 |
30.3 |
35.9 |
|
Rifampin |
0 |
0.1 |
0.1 |
|
Vancomycin |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Data
adapted from ref [61]
1. See
table 2 for definitions.
2. Similar
resistance rates observed with clarithromycin and azithromycin
Table 3. Representative
Peak Serum Concentrations of ß-Lactam Antibiotics in Reference to in
vitro Resistance in Adults.
|
Antibiotic
|
Definition
by MIC (μg/ml) 1 |
Mean peak
serum conc. in μg/ml 2
(Antibiotic dosage in g) |
Potency
relative to penicillin3 |
||
|
Susceptible |
Intermediate |
Resistant |
|||
|
Penicillin |
£ 0.06 |
0.1 - 1 |
³2 |
|
|
|
Amoxicillin |
£ 2 |
4 |
³ 8 |
7.5 (0.5) |
± |
|
Cefotaxime,
Ceftriaxone,
Cefepime:
non-meningitis
meningitis |
£ 1
£ 0.5 |
2
1 |
³ 4
³ 2 |
130 (2)
250 (2)
130 (2) |
+
+
+ |
|
Cefaclor |
£ 1 |
2 |
³ 4 |
16.5 (0.5) |
- - |
|
Cefprozil |
£ 2 |
4 |
³ 8 |
9.6-10.5
(0.5) |
-
- |
|
Cefpodoxime |
£ 0.5 |
1 |
³ 2 |
4.2 (0.4) |
- |
|
Ceftibuten |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
15.0 (0.4) |
- - |
|
Cefixime |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
1.9 (0.2) |
- - |
|
Cefuroxime
sodium (parenteral) |
£ 0.5 |
1 |
³ 2 |
100 (1.5)
|
- |
|
Cefuroxime
axetil (oral) |
£ 1 |
2 |
³ 4 |
4.4-9.0
(0.5) |
- |
|
Imipenem |
£ 0.12 |
0.25-0.5 |
³ 1 |
52 (1) |
++ |
|
Meropenem |
£ 0.25 |
0.5 |
³ 1 |
49 (1) |
+ |
1. Susceptibility definitions are from ref [150]
2. Serum concentration data were
obtained from ref[15, 64, 71,
118, 126, 168]
3. ±
indicates similar MICs; + indicates two- to four-fold lower MICs, ++
indicates 4-fold or lower MICs, - indicates two- to four-fold greater MICs,
and -- indicates 4-fold or greater MICs. N/A indicates that
interpretive criteria are not available
Table 3-a: Time Above MIC for Three Oral and Four Parenteral β-lactam Antibiotics Tested against Penicillin-Intermediate
and Penicillin-Resistant Strains of
Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
Drug |
Regimen |
S Pneumoniae (I) |
|
S pneumoniae (R) |
|
|
|
|
MIC 50-90 (ug/ML) |
Time above MIC (%) |
MIC 50-90 (ug/ML) |
Time above MIC (%) |
|
Amoxicillin |
13.3 mg/Kg, t.i.d. |
0.25-1 |
80-55 |
1-2 |
55-43 |
|
Cefaclor |
13.3 mg/Kg, t.i.d. |
8-16 |
20-0 |
32-64 |
0 |
|
Cefuroxime |
15 mg/Kg b.i.d |
0.5-2 |
56-40 |
4-8 |
30-0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ampicillin |
1 g q6h |
0.5-2 |
71-100 |
2-4 |
71-54 |
|
Penicillin |
2MU q6h |
0.5-1 |
58-66 |
2-4 |
50-41 |
|
Cefotaxime |
1g q8h |
0.25-1 |
87-63 |
1-2 |
63-52 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
1g q24h |
0.25-1 |
76-100 |
1-2 |
76-48 |
Table
4. Recommended Therapy for Penicillin-Susceptible and -Resistant
Pneumococcal Infections.
|
Infection
|
Empiric
Therapy1 |
Penicillin
susceptibility known |
||
|
Susceptible |
Intermediate
resistance |
PRSP |
||
|
Pneumonia or
bacteremia |
Penicillin
Ampicillin,
cefuroxime, amoxicillin, cefotaxime,
ceftriaxone |
Penicillin,
ampicillin, amoxicillin, cefuroxime |
Penicillin,
ampicillin, amoxicillin, cefuroxime |
High dose
penicillin
Cefotaxime,
ceftriaxone, high dose ampicillin,
Levofloxacin |
|
Meningitis |
Cefotaxime or
ceftriaxone + vancomycin2 |
Cefotaxime,
ceftriaxone, ampicillin or penicillin |
Cefotaxime3
or ceftriaxone + vancomycin2 |
Cefotaxime3
or ceftriaxone + vancomycin2 +
rifampin4, meropenem5 |
|
Otitis media |
Amoxicillin
in high dose6 |
Amoxicillin
|
Amoxicillin
in high dose6. (Avoid oral
cephalosporins) |
Amoxicillin
in high dose6, clindamycin,
ceftriaxone7 |
1. For
suspected pneumococcal infection or confirmed pneumococcal infection pending
susceptibility data.
2.
Vancomycin (15 mg/kg/dose 6-hourly in children) should be combined with a
cephalosporin in areas where cephalosporin resistance occurs.
Vancomycin therapy can be discontinued once the strain is confirmed to be
cephalosporin susceptible.
3. High
dosage (300 mg/kg/d) recommended.
4.
Addition of Rifampin (10 mg/kg/dose 12-hourly) should be
considered after 24 to 48 hours of therapy if the organism is susceptible to
rifampin and
1) the patient’s clinical condition has worsened; or 2) the subsequent
gram-stained smear or culture of CSF indicates failure to eradicate or to
reduce
substantially the number of organisms; or 3) the organism has a cefotaxime
or ceftriaxone MIC
³4
µg/ml.
5.
Meropenem may be considered for cephalosporin-resistant infections in
patients failing cephalosporin therapy although effectiveness has not been
established for such infections.
6. For
example, 90 mg/kg/day.
7. If oral therapy fails, intramuscular ceftriaxone can be given daily for 3 - 5 days.
Table 5: Antimicrobial
Therapy Recommendations for Children and Adults with Meningitis Caused by
Streptococcus pneumoniae on the
Basis of Susceptibility Tests Results
|
Drug* |
Pediatric Dose (mg
(u)/kg/day) |
adults Dose (total
daily dose) |
Dose interval |
Empirical therapy |
Penicillin susceptibility |
Cephalosporin resistant |
||
|
susceptible |
Intermediate resistant |
Resistant |
||||||
|
Penicillin |
G 250,000- 4000,000u# |
16- 24,000,000u |
4-6 h |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
Ampicillin |
200-400 mg |
8-12 gr |
4-6 h |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
|
Cefotaxime |
200-300 mg |
2.0 gr |
4-6 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes@ |
|
Ceftriaxone |
100 mg |
2.0 gr |
12 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes@ |
|
Vancomycin& |
60 mg |
2-3 gr |
6 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Rifampin |
20 mg |
600 mg |
12 h |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Yes@@ |
|
Cefepime |
150 mg |
6 gr |
8 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes@ |
|
Meropenem |
120 mg |
6 gr |
8 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Chloramphenicol |
75-100 mg |
4 gr |
6 h |
No |
No |
No |
No |
No@@@ |
* Duration of treatment
10-14 days
#1u= 0.6
μg/mL
&
Vancomycin should be given only in combination therapy
@
Combination therapy with vancomycin.
@@Addition
of Rifampin should be
considered after 24 to 48 hours of therapy if the organism is susceptible
to rifampin and 1) the patient’s clinical condition has worsened;
or 2) the subsequent gram-stained smear or culture of
CSF indicates failure to eradicate or to reduce substantially the number of
organisms; or 3) the organism has a
cefotaxime or ceftriaxone
MIC
> 4 µg/ml.
@@@ In
patients with sever Beta-lactam allergy should be considered in combination
therapy with vancomycin and addition of rifampin.
Table 6. Recommended
Daily Dosages of Agents Commonly Used for Treatment of Non-Meningeal
Pneumococcal Infections.
See
Table 4 For Selection Of Antibacterial
Agent.
|
Agent |
Route |
Adult Dosage
(g/day) |
Pediatric
Dosage
(mg/kg/day) |
Dosing
Interval (h) |
|
Penicillin |
IV |
4-12 million
U |
250,000-400,000 U/kg |
4-6 |
|
Ampicillin |
IV |
4-12 |
100-200 |
6 |
|
Cefazolin |
IV |
2-6 |
50-100 |
8 |
|
Cefuroxime |
IV |
2-4.5 |
100-150 |
6 |
|
Cefotaxime |
IV |
2-6 |
100-200 |
8 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
IV |
1-2 |
75-100 |
24 |
|
Vancomycin |
IV |
2 |
30-40 |
6-12 |
|
Levofloxacin |
IV/PO |
0.5 |
NE |
24 |
|
Gatifloxacin |
IV/PO |
0.4 |
NE |
24 |
|
Amoxicillin |
|
0.75-1.5 |
40-80 |
8 |
|
Cefuroxime |
|
0.5-1 |
100 |
12 |
|
Erythromycin |
|
1-2 |
40 |
6-8 |
|
Clarithromycin |
|
1 |
15 |
12-24 |
|
Azithromycin |
|
0.5 day 1
then 0.25 |
10 |
24 |
|
TMP/SMX |
|
0.16 |
8-12 (TMP) |
12 |
|
Clindamycin |
|
0.6-1.2 |
20-30 |
6-8 |
|
Moxifloxacin |
|
0.4 |
NE |
24 |
|
Telithromycin |
|
0.8 |
NE |
24 |
Use upper range dosages
of ß-lactam antibiotics to cover penicillin-resistant strains
IV, intravenous;
NE = Not established
Table 7. Serum And Middle
Ear Fluid Concentrations of Antimicrobial Agents that Have Been Used
for
Therapy of Childhood Otitis Media and
Comparative In Vitro Activity According to Pneumococcal Susceptibility to
Penicillin.
|
Antibiotic |
Dose (mg/kg) |
Peak
Concen-trations (μg/ml)1 |
MIC50,MIC90
(μg/ml) According to
Penicillin
Susceptibility2
|
|||
|
Serum |
MEF |
Susceptible |
Intermediate |
Resistant |
||
|
Amoxicillin |
15 |
13.6 |
5.6 |
0.01,
0.03 |
0.5, 1 |
4, 8 |
|
Cefaclor |
15 |
8.5 |
0.5 |
0.5, 1 |
4, 16 |
64, 64 |
|
15 |
16.8 |
3.8 |
||||
|
Cefixime |
8 |
2.5 |
1.3 |
0.25, 0.5 |
2, 32 |
32, 32 |
|
8 |
4.2 |
1.5 |
||||
|
Cefpodoxime |
5 |
2.0 |
0.2 |
0.03, 0.06 |
0.5, 2 |
4, 32 |
|
Cefprozil |
15 |
5.5 |
2.0 |
0.25, 0.25 |
1, 4 |
16, 32 |
|
15 |
12.1 |
2.0 |
||||
|
Ceftibuten |
9 |
6.7 |
4.0 |
4, 8 |
>32, >32 |
>32, >32 |
|
9 |
12.2 |
9.3 |
||||
|
Cefuroxime |
15 |
5.1 |
1.23 |
0.03, 0.12 |
1, 16 |
8, 16 |
|
Loracarbef |
15 |
9.3 |
3.9 |
1, 2 |
8, 32 |
32, 32 |
|
TMP/SMX |
4 |
2.0 |
1.4 |
0.25, 1 |
0.25, 4 |
2, 4 |
|
Erythromycin |
15 |
3.6 |
1.7 |
0.06, 0.06 |
0.25, 4 |
2, 16 |
|
Clarithromycin |
7.5 |
1.7 |
2.5 |
£ 0.03, 0.06 |
0.25, 8 |
1, 8 |
|
Azithromycin |
10®5 |
0.2 |
|
0.12, 0.12 |
2, 16 |
2, 32 |
|
10®5 |
|
9.4 |
||||
|
Ceftriaxone |
504 |
175 |
|
0.03, 0.06 |
0.012, 1 |
1.0, 2.0 |
MEF, middle
ear fluid; MIC50, median MIC; MIC90, concentration
inhibiting 90% of strains; TMP/SMX, trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole
1. Data from ref.
2. MIC data
are from middle ear isolates obtained from children in
Additional data are from isolates recovered from outpatients [61]
3. After a
single 250 mg dose in children aged 6 to 12 years.
4. Single intramuscular dose
Table 8: Antimicrobial
Therapy Recommendations for Children with Acute Otitis Media (AOM) caused by
Streptococcus pneumoniae
on the Basis of Susceptibility Tests
Results
|
Drug |
Dose (mg/kg/day ) |
Dose interval |
Penicillin susceptibility |
Macrolide resistant |
||
|
susceptible |
intermediate or
resistant |
|||||
|
First line |
Amoxicillin |
40-50 |
8 h |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Cefpodoxime proxetil |
10 |
12 h |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
|
Cefprozil |
30 |
12 h |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
|
Amoxicillin* |
70-90 |
8 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Second line** |
Amoxicillin/clavulanate |
45/6.4 |
12 h |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Amoxicillin/clavulanate* |
90/6.4 |
12 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Cefuroxime-axetil |
30 |
12 h |
Yes |
Moderate |
Yes |
|
|
Ceftriaxone*** |
50 |
24 h |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Type I allergy to
penicillins |
Erythromycin |
30-50 |
8 h |
Yes |
Yes@ |
No |
|
Clarithromycin |
15 mg |
12 h |
Yes |
Yes@ |
No |
|
|
Azithromycin& |
5-10 |
24 h |
Yes |
Yes@ |
No |
|
|
Clindamycin |
30-40 |
8 h |
Yes |
Yes@ |
Yes$ |
|
* If recurrent AOM episodes or if patient has
risk factors for infection with penicillin resistant S. pneumoniae
** If AOM persists after 48-72 hours of
treatment tympanocentesis should be recommended to make a bacteriologic
diagnosis.
@ In some
cases penicillin and macrolides S.
pneumoniae resistance are linked.
Table 9: Published
Reports on Mono vs. Combo in Treatment of Pneumonia (listed in the order of
time published)
|
Author/J/Time |
CAP vs pneumo |
Prospective /retrospective |
Patient number |
Controlled for severify
of illness Y/N |
Combo is superior Y/N |
|
Gleason Arch Int Med
1999 |
CAP |
R |
12,945 |
N |
Y |
|
Mufson AM J Med 1999 |
Bacteremic pneumococcal
pneumonia |
R |
328 |
N |
Y |
|
Waterer Arch Int Med
2001 |
Bacteremic pneumococcal
pneumonia |
R |
225, |
Y |
Y |
|
|
Bacteremic pneumococcal
pneumonia |
R |
409 |
N |
Y |
|
Weiss Can Respir J 2004 |
Bacteremic pneumococcal
pneumonia |
R |
95 |
Y |
Y |
|
Baddour Am J Respir
Crit Care Med 2004 |
bacteremia |
P |
844 |
Y |
Y |
|
Harbarth Eur J Clin
Miceobiol 2005 |
Pneumococcal sepsis |
R |
107 |
Y |
N |
|
Garcia Vazquez Eur J
Clin Micro 2005 |
CAP |
R |
1,391 |
Y |
Y |
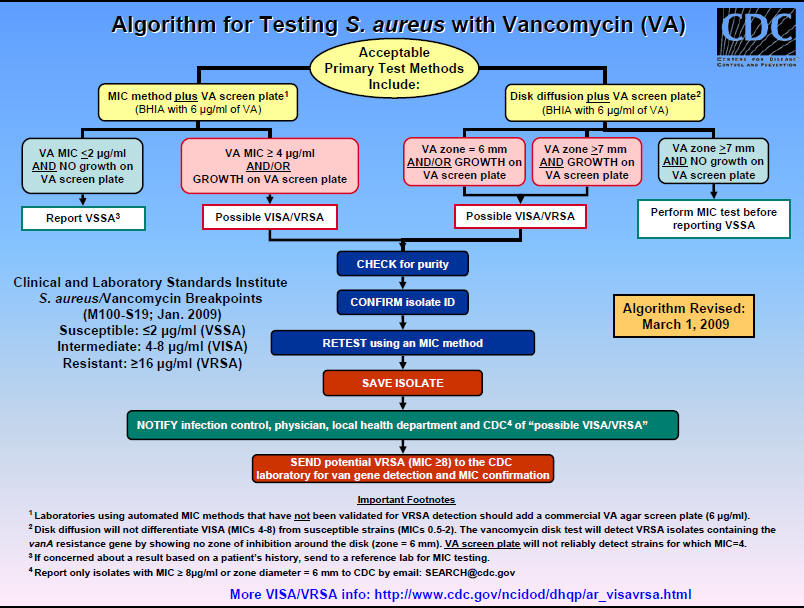
Figure 1: Algorithm for Testing Staphylococcus aureus Vancomycin Susceptibility (VISA or VRSA)
