Table 1: Comparison of Healthcare Associated and Community Associated MRSA
|
Characteristic |
Healthcare Associated-MRSA (HA-MRSA) |
Community Associated-MRSA (CA-MRSA) |
|
First Identified |
1961 |
1981 |
|
Antimicrobial Resistance |
Multidrug |
Only Beta-Lactams |
|
Clinical Manifestations |
More invasive (e.g., pneumonia, bloodstream infections) |
Less invasive (e.g., skin and soft tissue infections) |
|
Age of Patients |
Older |
Younger |
|
|
|
|
|
Molecular Typing Methods |
|
|
|
Pulse-field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) |
USA 100*, USA200, USA800 |
USA 300*, USA 400 |
|
SCCmec type |
II* I, III, IV |
IV*, V, VI |
|
Spa type |
t002*, t018 |
t008*, t128 |
|
Multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) |
ST35*, ST36 |
ST8*, ST1 |
|
Clonal Complex |
CC5*, CC30 |
CC8*, CC1 |
Table 2: In vitro Activity of Antimicrobial Agents Against Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
MIC against MSSA (μg/mL) |
MIC against MRSA (μg/mL) |
||||
|
Antibiotic |
Range |
50% |
90% |
Range |
50% |
90% |
|
Penicillins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Penicillin |
<0.06-128 |
16 |
128 |
32-128 |
64 |
128 |
|
Ampicillin |
2.0->32 |
>32 |
>32 |
4.0>32 |
>32 |
>32 |
|
Oxacillin |
0.25-2.0 |
0.5 |
1 |
16.0->128 |
>64 |
>128 |
|
Nafcillin |
0.25-1 |
0.5 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
Methicillin |
0.5-4 |
1 |
4 |
8->128 |
64 |
>64 |
|
Dicloxacillin |
0.06-0.5 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
Cephalosporins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cephalothin |
0.125-0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
4.0->32 |
>32 |
>32 |
|
Cefazolin |
0.5-4 |
1 |
2 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
Cephalexin |
4-16 |
8 |
16 |
128-256 |
>128 |
256 |
|
Cefaclor |
1-32 |
4 |
16 |
>64->128 |
128 |
>128 |
|
Cefuroxime |
0.5-2 |
1 |
2 |
64->128 |
>128 |
>128 |
|
Cefotaxime |
0.5->16.0 |
>16 |
>16 |
2.0->32 |
>32 |
>32 |
|
Cefepime |
1-8 |
4 |
4 |
8->64 |
64 |
>64 |
|
Ceftazidime |
4-16 |
8 |
16 |
16->64 |
64 |
>64 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
2-4 |
4 |
4 |
16->64 |
>64 |
>64 |
|
Cefoperazone |
2-4 |
2 |
4 |
32->256 |
>256 |
>256 |
|
Cefixime |
8-64 |
16 |
32 |
>32->64 |
>32 |
>64 |
|
Cefdinir |
0.125-1 |
0.25 |
1 |
0.5->64 |
64 |
>64 |
|
Cefpodoxime |
2-8 |
4 |
8 |
>64->128 |
>64 |
>128 |
|
Flomoxef |
0.12-4 |
0.5 |
4 |
8->32 |
>32 |
>32 |
|
Moxalactam |
2-16 |
8 |
16 |
>32 |
>32 |
>32 |
|
Cefpirome |
0.50-2 |
1 |
2 |
32-128 |
128 |
128 |
|
ß-lactam/ß-lactam inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amoxicillin/clavulanate |
0.12-2 |
1 |
2 |
16-64 |
32 |
64 |
|
Ampicillin/sulbactam |
0.06-2 |
1 |
2 |
8-32 |
32 |
32 |
|
Piperacillin-tazobactam |
0.06-32 |
1 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
Carbapenems |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meropenem |
0.06-1 |
0.12 |
0.12 |
0.5-16 |
8 |
>8 |
|
Imipenem |
0.12-0.5 |
0.12 |
0.25 |
0.05->16.0 |
4 |
16 |
|
Glycopeptides |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vancomycin |
0.25-2 |
1 |
2.0 |
0.24-4.0 |
2 |
2.0 |
|
Teicoplanin |
0.25-4.0 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5-4.0 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
|
Oritavancin |
0.12-0.5 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
0.12-1.0 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
Macrolides |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erythromycin |
0.13-4 |
0.25 |
4 |
0.06->32 |
>32 |
>32 |
|
Azithromycin |
0.25-8 |
1 |
4 |
>128 |
>128 |
>128 |
|
Clarithromycin |
0.13-4 |
0.25 |
1 |
0.125->64 |
>64 |
>64 |
|
Dirithromycin |
0.25-8 |
0.5 |
4 |
>64 |
>64 |
>64 |
|
Roxithromycin |
0.13-0.16 |
0.5 |
4 |
>64 |
>64 |
>64 |
|
Lincosamides, Streptogramins and Ketolides |
||||||
|
Clindamycin |
<0.06-0.125 |
0.125 |
0.125 |
>256 |
>256 |
>256 |
|
Quinuprisitin-Dalfopristin |
0.25 |
0.5 |
0.25-1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.25-1 |
|
Telithromycin |
0.015-32 |
0.06 |
0.25 |
0.03->128 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
Aminoglycosides |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gentamicin |
0.06-16 |
0.12 |
0.5 |
0.06-64 |
1 |
32 |
|
Tobramycin |
0.06-32 |
0.125 |
0.25 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
Amikacin |
0.5-4 |
1 |
2 |
2-64 |
16 |
32 |
|
Quinolones |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ofloxacin |
0.12-1 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.25-32 |
8.0 |
16 |
|
Pefloxacin |
0.12-2 |
0.5 |
1 |
0.25-128 |
32 |
128 |
|
Rufloxacin |
1.0-16 |
1.0 |
4.0 |
1.0->32 |
1.0 |
4.0 |
|
Sparfloxacin |
<0.015-0.12 |
0.03 |
0.12 |
<0.015-16 |
4 |
16 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
0.03-4.0 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
0.25->128 |
32 |
64 |
|
Norfloxacin |
0.25-1.0 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
0.25->32 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
|
Levofloxacin |
0.06-0.25 |
0.13 |
0.25 |
0.25-32 |
0.5 |
16 |
|
Moxifloxacin |
0.016-0.13 |
0.03 |
0.06 |
0.016-8 |
0.06 |
4 |
|
Gatifloxacin |
0.03-0.25 |
0.06 |
0.13 |
0.03-16 |
0.13 |
16 |
|
Trovafloxacin |
0.008-0.013 |
0.03 |
0.06 |
0.016-8 |
0.013 |
4 |
|
Clinafloxacin |
0.008-0.06 |
0.03 |
0.06 |
0.03-16 |
0.06 |
8 |
|
Gemifloxacin |
0.008-16 |
0.016 |
0.03 |
0.016-16 |
2 |
8 |
|
Sitafloxacin |
0.008-4 |
0.015 |
0.03 |
0.015-8 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
Miscellaneous |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tetracycline |
0.006-124 |
0.25 |
64 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
Trimethoprim |
0.06-0.25 |
0.125 |
0.25 |
0.25-1 |
0.5 |
1 |
|
Sulfamethoxazole |
1.19-4.75 |
2.38 |
4.75 |
4.75-19 |
9.5 |
19 |
|
Fusidic acid |
0.06-0.12 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
0.03-8 |
0.06 |
0.06 |
|
Rifampin |
<0.03->16 |
<0.03 |
1.0 |
<0.03->16 |
>16 |
>16 |
|
Mupirocin |
0.06-2 |
0.25 |
0.25 |
0.125->256 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
Linezolid |
0.5-1 |
1 |
1 |
0.5-1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Daptomycin |
≤0.12-2 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
≤0.12-1 |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
Tigecycline |
0.25-0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.25-1 |
0.5 |
1 |
aMSSA: Methicillin-susceptible S. aureus; MRSA: Methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
Table 3. Suggested Antibiotics, Doses
and Duration for Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infections
|
Infection type |
Penicillin allergy status |
Initial IV regimen |
Subsequent oral regimen |
Total duration of therapy |
|
Catheter-related bacteremia and Cellulitis |
|
|
||
|
MSSA |
Penicillin non-allergic |
Nafcillin or oxacillin 50mg/kg
up to 2g q4h |
Oral cloxacillin, flucloxacillin or dicloxacillin at same dose |
2 weeks |
|
|
Minor penicillin allergy |
Cephalothin 50mg/kg up to 2g
q6h |
Oral cephalexin 1g q6h |
2 weeks |
|
|
Life-threatening penicillin-allergy |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h |
Oral rifampin 600mg daily plus ciprofloxacin 750mg bid or fusidic acid 500mg bid |
2 weeks |
|
MRSA |
Any of the above |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h |
Oral rifampin 600mg daily plus ciprofloxacin 750mg or fusidic acid 500mg bid |
2 weeks |
|
Meningitis |
|
|
|
|
|
MSSA |
Penicillin non-allergic |
Nafcillin or oxacillin 50mg/kg
up to 2g q4h |
Not recommended |
4weeks |
|
|
Penicillin-allergy |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h |
Not recommended |
4weeks |
|
MRSA |
Any of the above |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h plus rifampin 600mg IV or orally daily |
Not recommended |
|
|
Acute osteomyelitis, Septic arthritis, Pneumonia, Lung abscess |
|
|||
|
MSSA |
Penicillin non-allergic |
Nafcillin or oxacillin 50mg/kg
up to 2g q4h |
Oral cloxacillin, flucloxacillin or dicloxacillin at same dose |
4weeks |
|
|
Minor penicillin allergy |
Cephalothin 50mg/kg up to 2g
q6h |
Oral cephalexin 1g q6h |
4weeks |
|
|
Life-threatening penicillin-allergy |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h |
Oral rifampin 600mg daily plus ciprofloxacin 750mg bid or fusidic acid 500mg bid |
4 weeks |
|
caMRSA |
Any of the above |
Clindamycin 10mg/kg up to 450mg q8h |
Oral clindamycin 10mg/kg up to 450mg q8h |
4 weeks |
|
haMRSA |
Any of the above |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h |
Oral rifampin 600mg daily plus ciprofloxacin 750mg bid or fusidic acid 500mg bid |
4 weeks |
|
Chronic osteomyelitis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As for acute osteomyelitis |
As for acute osteomyelitis |
3 to 12 months |
|
Prosthetic joint infection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As for septic arthritis |
As for septic arthritis |
6 to 8 weeks IV followed by 6 to12 weeks oral |
Table 4: Most Commonly Recommended
Treatment Regimens for Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis
|
Infection type |
Penicillin allergy status |
Regimen |
||||||
|
Left-sided infection with penicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (PSSA) |
||||||||
|
Native valve |
Penicillin non-allergic |
Penicillin G 45mg/kg up to 1.8g q4h IV for 4-6 weeks±gentamicin for 5 days |
|
|||||
|
|
Minor penicillin allergy |
First-generation cephalosporin e.g. cephalothin 50mg/kg up to 2g q4h IV or cefazolin 50mg/kg 2g q8h IV for 4-6 weeks±gentamicin for 5 days |
|
|||||
|
|
Life-threatening penicillin-allergy |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h for 4-6 weeks±gentamicin for 5 days* |
|
|||||
|
Prosthetic valve |
Any of the above |
Add rifampin 15mg/kg up to 600mg q24h orally and give gentamicin for 2 weeks |
|
|||||
|
Left-sided infection with methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) |
|
|||||||
|
Native valve |
Penicillin non-allergic |
Penicillinase-resistant penicillin e.g. nafcillin/oxacillin 2g q4h for 4 weeks± gentamicin 1mg/kg q8h for 5 days |
|
|||||
|
|
Minor penicillin allergy |
First-generation cephalosporin e.g. cephalothin 2g q4h or cefazolin 2g q8h for 4-6 weeks±gentamicin for 3 to 5 days |
|
|||||
|
|
Life-threatening penicillin-allergy |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h for 4-6 weeks±gentamicin for 3 to 5 days |
|
|||||
|
Poor response |
Any of the above |
Add rifampin* |
|
|||||
|
Prosthetic valve |
Any of the above |
Add rifampin and give gentamicin for 2 weeks |
|
|||||
|
Left-sided infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) |
|
|||||||
|
Native valve |
All |
Vancomycin 25mg/kg up to 1g q12h for 4-6 weeks±gentamicin for 3 to 5 days |
|
|||||
|
Poor response |
All |
Add rifampin* |
|
|||||
|
Prosthetic valve |
All |
Add rifampin and give gentamicin for 2 weeks |
|
|||||
|
Right-sided infection (non-prosthetic) |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Above regimens for 2 weeks or oral ciprofloxacin+rifampin for 4 weeks if no other infection focus |
|
|||||
* Daptomycin 6mg/kg daily
Table 5: Isolation
Precautions Recommended for Hospitalized Patients
Standard precautions
· Wash hands after touching blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, or contaminated items, whether or not gloves are worn; wash hands promptly upon removing gloves and between patient contacts
· Use plain (nonantimicrobial) soap for routine handwashing
· Use antimicrobial soap or waterless antiseptic agent for special circumstances (e.g. for control of outbreaks)
· Wear clean, nonsterile gloves when touching blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions
or contaminated items; remove gloves immediately after use
· Wear a clean, nonsterile gown during procedures and patient-care activities that are likely to generate splashes or sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions or excretions; remove gown as soon as possible, and wash hands
· Wear a mask and eye protection or face shield during procedures that are likely to generate splashes or sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions or excretions
· Handle contaminated patient-care equipment carefully, and ensure that reusable equipment is cleaned appropriately before it is used for another patient
· Housekeeping personnel should routinely clean environmental surfaces of beds, bedrails, bedside equipment, and other frequently touched items
· Handle soiled linen in a manner that prevents skin exposure and contamination of clothing
Contact precautions
· Place patient in a private room or in a room with another patient who is infected with the same organisms (cohorting)
· Wear clean nonsterile gloves when entering patient’s room
· Change gloves during course of care and after contact with infective material
· Remove gloves upon leaving patient’s room
· Wash hands with an antimicrobial soap or waterless antiseptic agent after removing gloves
· Wear a gown when entering room if substantial contact with the patient or environmental surfaces in the room are anticipated, or if the patient has wound drainage not contained by a dressing; remove gown before leaving patient’s room
· Limit transport of patient from the room to essential purposes only
· When possible, dedicate the use of noncritical equipment to a single patient or cohort of patients; if use for another patient is unavoidable, adequately clean and disinfect item before use for another patient
· No special precautions are needed for dishes, glasses and other eating utensils
From Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Table 6:
Recommendations to Prevent The Spread of Vancomycin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus
· The laboratory should immediately notify infection-control personnel on the clinical unit, and the attending physician
· Infection-control personnel, in collaboration with appropriate authorities, including the state health department and the CDC, should initiate an epidemiologic and laboratory investigation
Medical and Nursing Staff Risks
· Isolate the patient in a private room and use contact precautions (gown, mask, gloves, and antibacterial soap for hand washing) recommended for multidrug-resistant microorganisms
· Minimize the number of persons with access to colonized/infected patients
· Dedicate specific healthcare workers to provide one-on-one care of the colonized/infected patient or the cohort of colonized/infected patients
Infection Control Personnel Tasks
· Inform all personnel providing direct patient care of the epidemiologic implications of such strains and of the infection control precautions necessary for their containment
· Monitor and strictly enforce compliance with contact precautions and other recommended infection control practices
· Determine whether transmission has already occurred by obtaining baseline cultures (before initiation of precautions) for staphylococci with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin from nares and hands of all healthcare workers, roommates, and others with direct patient contact
· Assess efficacy of precautions by monitoring healthcare personnel acquisition of staphylococci with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin as recommended by consultants to the state health department or CDC
· Avoid transferring infected patients within or between facilities and, if transfer is necessary, fully inform the receiving institution or unit of the patient’s colonization/infection status and appropriate precautions
· Consult with the state health department and CDC before discharge of a colonized/infected patient
Skin-to-skin contact is the primary mode of transmission, thus personal hygiene is very important.
A. The washing machine should not be overloaded.
B. Consider the 1) mechanical action of the machine, 2) water flow, 3) water
temperature, 4) time and 5) chemicals used.
C. Sodium hypochlorite (chlorine bleach) is the disinfectant of choice for
clothing. If the clothing is made of polyester/cotton, chlorine alternatives
may be used. However, bleach is the optimal choice if the fabric allows.
D. Clothes can be washed with regular detergent.
E. Dry clothes in a hot temperature dryer as opposed to air-drying.
1. Cover a wound with a clean dry dressing so that any drainage is contained.
2. Use clothes or towels as a barrier between your skin and equipment.
3. Cover scrapes/cuts with a clean dressing until healed.
4. Avoid contact with another person’s wound or dressing.
5. Wound dressings can be placed in the regular trash.
6. Wash hands after each dressing change.
7. A physician should drain abscesses and obtain a culture.
8. Do not use antibiotics until the culture is taken and results are known.
9. Do not share antibiotics.
10. Take the antibiotic as prescribed. Do not hoard or self-medicate.
11. Place used dressings in a disposable plastic bag, tie, and discard.
1. Infected individuals should receive hand washing and other personal hygiene instructions as related to transmission between players. Skin-to-skin contact is the mode of transmission.
2. Use of antibiotics should be reviewed with the athlete if it is prescribed.
3. Trainers and players should be educated concerning MRSA transmission and prevention.
4. The health department should be notified if MRSA infections occur (if required in that state).
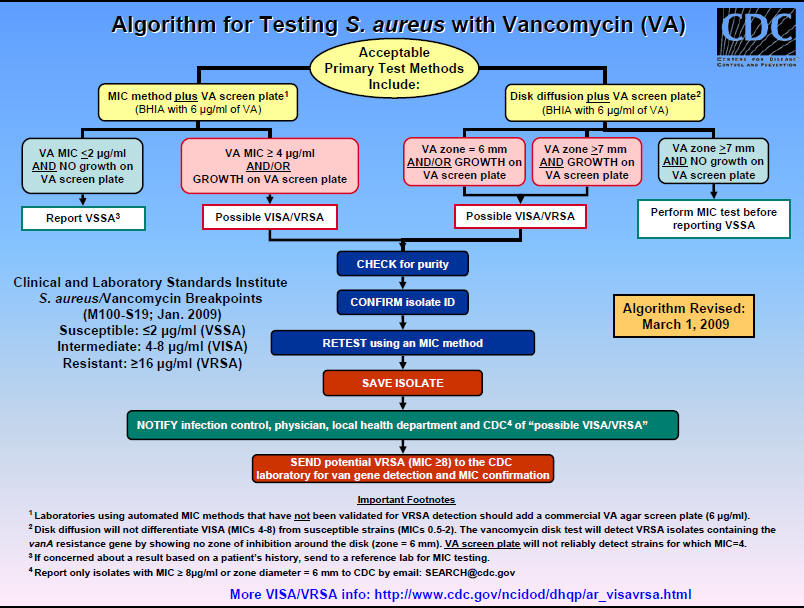
Figure 1: Algorithm for Testing Staphylococcus aureus Vancomycin Susceptibility (VISA or VRSA)
