Table 1. Extra-intestinal Infectious Complications of Typhoid Fever Caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi
|
Organ system involved |
Prevalence |
Risk factors |
Complications |
|
Central Nervous System |
3-35% |
Residence in endemic region,217 malignancy,218 endocarditis, congenital heart disease, paranasal sinus infections, pulmonary infections, meningitis, trauma, surgery, and osteomyelitis of the skull |
Encephalopathy,219 cerebral edema,217 subdural empyema,220 cerebral abscess,218, 221 meningitis,222 ventriculitis, transient Parkinsonism, motor neuron disorders, ataxia,20 seizures, Guillain-Barré syndrome, psychosis223 |
|
Cardiovascular |
1-5% |
Cardiac abnormalities such as existing valvular abnormalities, rheumatic heart disease or congenital heart defects224 |
Endocarditis,225, 226,227,228myocarditis,223 pericarditis,229 arteritis, congestive heart failure230 |
|
Pulmonary |
1% |
Residence in endemic region, past pulmonary infection, sickle cell anemia, alcohol abuse, diabetes, HIV infection30 |
Pneumonia,30, 231 empyema,232 bronchopleural fistula, infected pulmonary hydatid cyst233 |
|
Bone and Joint |
< 1% |
Sickle cell anemia, diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, lymphoma, liver disease, previous surgery or trauma, those at extremes of age, and steroid use234 |
Osteomyelitis,62, 223, 234,235,236,237,238,239 septic arthritis240 |
|
Hepatobiliary |
1-26% |
Residence in endemic region, pyogenic infections, intravenous drug use, splenic trauma, HIV, hemoglobinopathy |
Cholecystitis, hepatitis,223, 241 hepatic abscesses242, splenic abscess,243, 244,245 peritonitis, paralytic ileus223 |
|
Genitourinary |
<1% |
Urinary tract, pelvic pathology and systemic abnormalities |
Urinary tract infection,55, 246 renal abscess, pelvic infections,247 testicular abscess, prostatitis, epididymitis |
|
Soft tissue infections |
17 cases reported in the English literature |
Diabetes248 |
Psoas abscess 248, 249 gluteal abscess,250 cutaneous vasculitis,251 |
|
Hematologic |
5 cases reported in the English literature |
|
Abbreviations: HIV – human immunodeficiency virus
Table 2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (μg /ml) for Selected Antibiotics Against Salmonella typhi
|
|
"Sensitive isolates" |
"MDR isolates" |
||
|
|
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
|
Penicillin G |
4 |
8 |
|
|
|
Ampicillin |
0.5 |
1.0 |
>256 |
>256 |
|
Amoxicillin-Clavulanic acid |
0.5 |
1.0 |
8 |
8 |
|
Piperacillin |
0.5 |
1 |
|
|
|
Piperacillin-Tazobactam |
0.5 |
1 |
|
|
|
Ticarcillin |
2 |
4 |
|
|
|
Azlocillin |
8 |
8 |
|
|
|
Mezlocillin |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
Mecillinam |
0.125 |
0.125 |
1* |
2* |
|
Cefuroxime |
2 |
4 |
|
|
|
Cefoperazone |
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
Cefoxitin |
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
Ceftriaxone |
0.06 |
0.125 |
0.06 |
0.125 |
|
Ceftazidime |
0.25 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
Cefepime |
0.06 |
0.125 |
|
|
|
Cefpirome |
0.06 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
Cefixime |
0.06 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
Ceftizoxime |
0.06 |
0.125 |
|
|
|
Aztreonam |
0.125 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
Imipenem |
0.25 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
Meropenem |
0.06 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
Azithromycin |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
|
Rifampicin |
8 |
16 |
|
|
|
Trimethoprim |
0.125 |
0.25 |
128 |
>256 |
|
Sulfamethoxazole |
4 |
16 |
>256 |
>256 |
|
Chloramphenicol |
4 |
8 |
>256 |
>256 |
|
Tetracycline |
1 |
1 |
>256 |
>256 |
|
Gentamicin |
0.25 |
2.0 |
|
|
|
Nalidixic acid |
4 |
8 |
4 |
8 |
|
Norfloxacin |
0.06 |
0.25 |
0.06 |
0.25 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
0.015 |
0.03 |
0.015 |
0.03 |
|
Ofloxacin |
0.06 |
0.125 |
0.06 |
0.125 |
|
Pefloxacin |
0.125 |
0.125 |
0.125 |
0.125 |
Table 3. Fluoroquinolone Efficacy in Enteric Fever
|
Drug |
Reference |
Dosage |
Patients |
Clinical cure % |
Micro cure % |
FCT (days) |
Relapse Rate % |
|
Ofloxacin |
Morelli et al 1992120 |
300 mg tid 15 days |
30 |
100 |
100 |
2.6 |
0 |
|
Pefloxacin |
Morelli et al 1992120 |
400 mg tid 15 days |
36 |
100 |
100 |
3.7 |
0 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Morelli et al 1992120 |
500 mg tid 15 days |
20 |
100 |
100 |
3.3 |
0 |
|
Enoxacin |
Morelli et al 1992120 |
300 mg tid 15 days |
20 |
80 |
80 |
4.6 |
0 |
|
Norfloxacin |
Morelli et al 1992120 |
400 mg tid |
20 |
60 |
60 |
4.6 |
0 |
|
Norfloxacin |
Sarma & Durairaj 1991121 |
400mg bid 7 days |
20 |
100 |
100 |
3.7 |
0 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Uwayda et al 1992254 |
500mg bid, 7-10 days |
34 |
100 |
100 |
4.9 |
0 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Uwayda et al 1992254 |
750mg bid, 7-10 days |
28 |
100 |
100 |
5.2 |
4 |
|
Fleroxacin |
Arnold et al 1993145 |
400mg od, 7 days |
28 |
83 |
96 |
4 |
17 |
|
Fleroxacin |
Arnold et al 1993145 |
400mg od, 14 days |
35 |
100 |
97 |
4 |
0 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Wallace et al 1993161 |
500mg bid, 7 days |
20 |
100 |
100 |
4 |
0 |
|
Fleroxacin |
Hien et al 1994159 |
400mg od, 7 days |
15 |
100 |
100 |
3.4 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Smith et al 1994160 |
200mg bid, 5 days |
22 |
100 |
100 |
3.4 |
0
|
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Alam et al 199576 |
500mg bid, 10 days |
35 |
100 |
100 |
4.2 |
0 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Alam et al 199576 |
500mg bid, 14 days |
34 |
100 |
100 |
4.9 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Smith et al 1995160 |
15mg/kg/d 3 days |
118 |
100 |
100 |
2.5 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Smith et al 1995160 |
10mg/kg/d 5 days |
110 |
100 |
100 |
3.0 |
1 |
|
Fleroxacin |
Duong et al 1995255 |
400mg od, 5 days |
41 |
97.5 |
100 |
3.4 |
4 |
|
Fleroxacin |
Duong et al 1995255 |
400mg od, 3 days |
22 |
100 |
100 |
3.7 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Vinh et al 1996162 |
15mg/kg/d 3 days |
47 |
96 |
100 |
4.5 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Vinh et al 1996162 |
15mg/kg/d 2 days |
53 |
89 |
98 |
4.5 |
2 |
|
Pefloxacin |
Unal et al 1996256 |
400mg bid 7 days |
24 |
100 |
100 |
3.4 |
4 |
|
Pefloxacin |
Unal et al 1996256 |
400mg bid 5 days |
22 |
100 |
96 |
3.1 |
0
|
|
Ofloxacin |
Chinh et al 1997135 |
15mg/kg/d 3 days |
53 |
89 |
100 |
4.0 |
2 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Chinh et al 1997135 |
15mg/kg/d 2 days |
47 |
98 |
98 |
4.0 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Secmeer et al 1997257 |
40mg/kg/d |
24 |
100 |
100 |
3.3 |
0 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Girgis et al 1999258 |
500mg bid 7 days |
28 |
100 |
100 |
3.3 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Cao et al 1999259 |
10mg/kg/d 5 days |
38 |
97 |
100 |
4.4 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin* |
Chinh et al 200079 |
8mg/kg/d 5 days |
44 |
86 |
95.5 |
5.6 |
5 |
|
Ciprofloxacin |
Gasem et al 200370 |
500mg/d 7d |
28 |
96 |
82 |
5.1 |
0 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Vinh et al 2005170 |
10mg/kg/d 3 days |
107 |
95.3 |
99.1 |
4.21 |
2.8 |
|
Ofloxacin |
Vinh et al 2005170 |
10mg/kg/d 2 days |
89 |
91.3 |
95.5 |
3.83 |
2.2 |
* 48% of the infections were quinolone resistant
Table 4. Third Generation Cephalosporin Efficacy In Enteric Fever Drug
|
|
Reference |
Dosage |
No of patients |
Clinical Cure (%) |
Micro Cure (%) |
mean (SD) FCT(days) or range |
Relapse Rate(%) |
|
Cefotaxime |
Soe et al 1987115 |
200mg/kg /day 6-14 d |
61 |
82 |
|
|
6 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Islam et al 1988149 |
3-4g/day, 7 d |
32 |
91 |
100 |
4->14 |
6 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Lasserre et al 1991260 |
3g/day,3 d |
19 |
95 |
100 |
3-13 |
11 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Lasserre et al 1991260 |
4g/day, 3 d |
20 |
100 |
100 |
4-11 |
0 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Wallace et al 1993161 |
3g/day, 7 d |
22 |
73 |
100 |
5.2 |
5 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Islam et al 1993149 |
4g/day, 5 d |
28 |
79 |
100 |
|
4 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Tran et al 1994159 |
2g/day, 5 d |
15 |
87 |
93 |
6.7 |
0 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Smith et al 1994160 |
3g/day, 3 d |
25 |
72 |
92 |
8.2 |
4 |
|
Ceftriaxone |
Bhutta et al 199477 |
65mg/kg /day, 14 d |
25 |
88 |
88 |
8.0 |
14 |
|
Cefixime |
Bhutta et al 199477 |
20mg/kg /day, 12+ d |
50 |
100 |
100 |
5.3 |
4 |
|
Cefixime |
Girgis et al 1994158 |
10mg/kg /day, 14 d |
25 |
88 |
96 |
8.3 |
4 |
|
Cefixime |
Girgis et al 1995178 |
7.5mg/kg bid, 14d |
50 |
100 |
100 |
5.3 |
6
|
|
Ceftriaxone |
Girgis et al 1995178 |
50-70mg/kg daily, 5 d |
43 |
100 |
100 |
3.9 |
5
|
|
Cefixime |
Rabbani et al 1998261 |
10mg/kg/d 14d |
20 |
90 |
90 |
|
6
|
|
Cefixime |
Cao et al 1999259 |
20mg/kg/d 7d |
44 |
75 |
90 |
8.5 |
2
|
|
Ceftriaxone |
French et al 2000262 |
75mg/kg/d 7d |
30 |
97 |
97 |
3.9 |
13
|
|
Ceftriaxone |
Bhutta et al 2000171 |
6mg/kg/d 7d |
29 |
93 |
100 |
5.4 |
4
|
|
Ceftriaxone |
Bhutta et al 2000171 |
65mg/kg/d 14d |
28 |
96 |
100 |
5.2 |
0
|
|
Ceftriaxone |
Frenck et al 2004263 |
75mg/d 5d |
36 |
81 |
97 |
3.6 |
14 |
FCT = Fever clearance time
Table 5. Azithromycin Efficacy In Enteric Fever
|
Reference |
Dosage |
Patients |
Clinical cure % |
Micro cure % |
FCT (days) |
Relapse Rate % |
|
Butler et al 1999264 |
9.6 mg/kg/d 7 days |
42 |
88 |
100 |
4.1 |
0 |
|
Girgis et al 1999258 |
16 mg/kg followed by 8 mg/kg total 7 days |
36 |
100 |
100 |
3.8 |
0 |
|
Chinh et al 200079 |
20 mg/kg/d 5 days |
44 |
96 |
98 |
5.5 |
0 |
|
Frenck et al 2000262 |
10 mg/kg/d 7 days |
34 |
91 |
97 |
4.1 |
0 |
|
Frenck et al 2004263 |
20 mg/kg/d 5 days |
32 |
100 |
100 |
4.5 |
0 |
Table 6. Antibiotics of Choice [Download PDF]
|
|
Endemic area |
Non-immune |
|
Uncomplicated enteric fever |
Ofloxacin or ciprofloxacin orally 7.5mg/kg b.i.d or levofloxacin orally 500mg daily for 3-5 days* |
Ofloxacin or ciprofloxacin orally 7.5mg/kg b.i.d or levofloxacin orally 500mg daily for 5-7 days* |
|
Severe typhoid** |
Ofloxacin or ciprofloxacin 7.5mg/kg infused over 30-60 minutes every 12 hours or levofloxacin 500mg infused every 24 hours until oral treatment can be substituted. Continue same dose for 10-14 days. |
Ofloxacin or ciprofloxacin 7.5mg/kg infused over 30-60 minutes every 12 hours or levofloxacin 500mg infused every 24 hours until oral treatment can be substituted. Continue same dose for 10-14 days. Immunocompromised patients should receive at least three weeks treatment. |
|
Carriers |
Adults: Ofloxacin or Ciprofloxacin orally 7.5 mg/kg b.i.d. or levofloxacin orally 500mg daily for 4 weeks. Children: Amoxicillin 10mg/kg/day for 6-8 weeks plus probenecid |
|
*Pefloxacin or fleroxacin have both proved very effective as well (Table 2). The three days course is particularly useful in epidemic
containment.
**Dexamethasone 3mg/kg I.V. stat followed by 1mg/kg six hourly for 48 hours should be given to patients with encephalopathy or
shock unrelated to perforation or hemorrhage. For quinolone resistant infections substitute ceftriaxone.
Alternative Treatments
|
|
Uncomplicated enteric fever |
Severe typhoid |
|
Chloramphenicol |
75mg/kg/day in 4 divided oral doses for 14 days |
Chloramphenicol succinate 75mg/kg/day I.V. or I.M. in 4 divided doses until oral treatment can be substituted. Then 50mg/kg/day orally for 14-21 days
|
|
Ampicillin/amoxicillin |
Amoxicillin 75-100mg/kg/day in 3-4 divided oral doses for 14 days
|
Ampicillin 15mg/kg/day I.V. in 4 divided doses for 14-21 days |
|
Trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole |
8/40 mg/kg/day in 2 divided oral doses (corresponding in adults to 2-3 tablets b.i.d.) 14 days. |
Intravenous dose regimen similar to the oral regimen |
|
Cefixime/ceftriaxone |
Cefixime 20mg/kg/day in 4 divided oral doses for 7-10 days |
Ceftriaxone 60 mg/kg/day I.V. or I.M. for at least 5 days, then if possible switch to oral therapy to complete 14-21 days treatment |
Table 7. Typhoid Vaccines [Download PDF]
|
Vaccine |
Dose |
Adverse effects |
Comments |
|
Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine |
Single dose 0.5mL of 50 µg/mL vaccine by I.M. or deep S.C. injection |
Local pain, erythema and fever may occur 1-3 days after administration. |
Children < 18 months may show sub-optimal response. Repeat every 3 years |
|
Ty 21a oral live attenuated vaccine |
1 capsule to be swallowed with cold or lukewarm drink on days 1, 3, and 5 |
Usually none. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, headache, fever, allergic reactions. Rarely: anaphylaxis. |
Contraindicated in patients who are immunosuppressed either by disease or drugs Inactivated by antibiotics Capsules must be refrigerated. Not recommended for children <6 years. Provides protection 7-10 days after last dose, and in endemic areas this lasts for 3 years in most cases, but for travelers who are not repeatedly exposed, protection may last for only one year. Do not give mefloquine until 3 days after last dose, and administration of oral polio vaccine should be separated by at least three weeks |
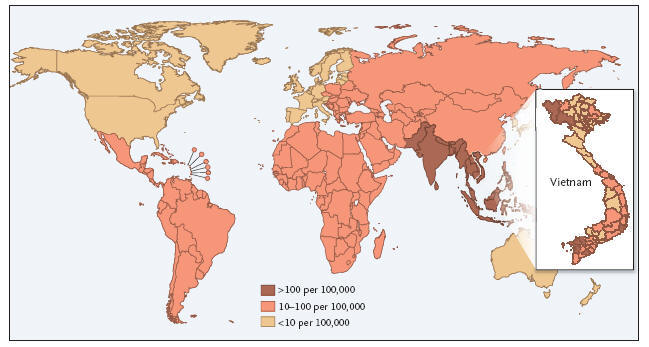
Figure 1: 1,000 Cases per 100,000 Population per Year.
