
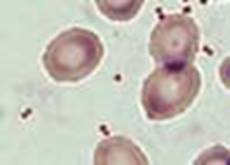
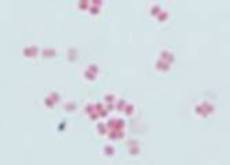








Neisseria meningitidis, N. gonorrhoeae, and Moraxella catarrhalis
Chocolate, BAP, & Nutrient agar needed for good identification
@ Ellen Jo Baron 2007
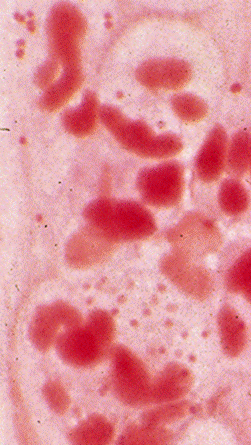

▪ All 3 major gram neg diplococci grow well on chocolate agar
▪ N. meningitidis and Moraxella catarrhalis grow on BAP and nutrient agar
▪ M. catarrhalis grows at 22°C on BAP; N. meningitidis does not
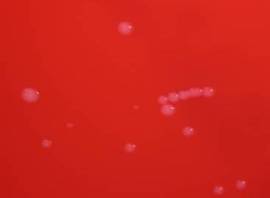
In original specimen:
Gram negative diplococci, some intracellular