



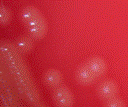
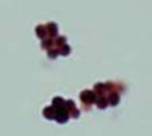

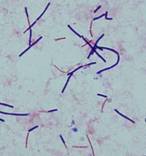
Micrococcus








![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
@ Ellen Jo Baron 2007




Slide coagulase test: The slide Coagulase test
detects bound coagulase (clumping factor). This type of coagulase is
attached ot the bacterial cell walls (surface). This test is usually
performed on a glass slide.