



Pathogen in blood, lymph nodes, bone marrow


![]()



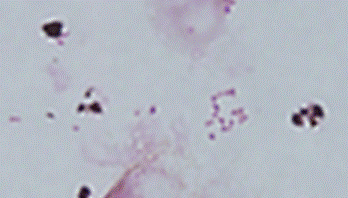
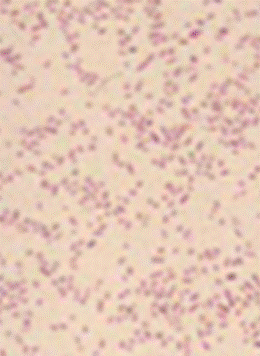
Gram stain: The Gram stain, is a laboratory staining technique that distinguishes between two groups of bacteria that have differences in the structure of their cell walls. Standard bacterial taxonomy makes a distinction between Gram-negative bacteria, which stain red/pink and the Gram-positive bacteria, which stain blue/purple. Different antimicrobial agents are directed specifically at gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria.
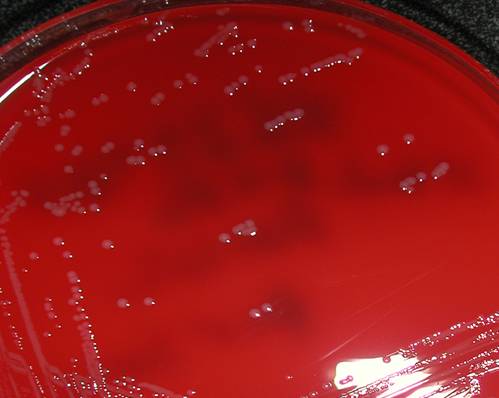
Pathogen in bite wounds, blood
- Do not grow on MacConkey
-
Non-hemolytic, good growth on BAP-
Catalase positive-
Oxidase positive-
Indole positive - rapid - Urease negative- Smells like bleach
![]()

![]()
![]()